2-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde
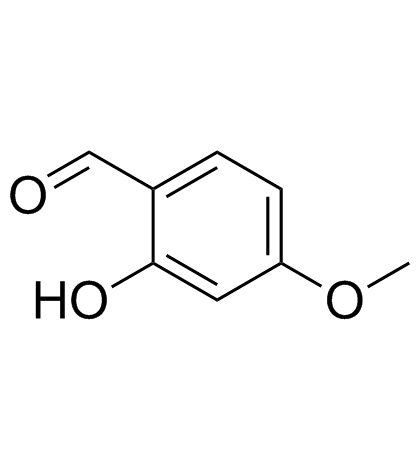
2-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde structure
|
Common Name | 2-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 673-22-3 | Molecular Weight | 152.15 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 271.5±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H8O3 | Melting Point | 41-43 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 112.1±15.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of 2-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde2-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde, a chemical compound and an isomer of Vanillin, could be used to synthesis Urolithin M7[1]. 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde is a potent tyrosinase inhibitor from three East African medicinal plants, Mondia whitei, Rhus vulgaris Meikle, and Sclerocarya caffra Sond[2]. |
| Name | 2-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 2-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde, a chemical compound and an isomer of Vanillin, could be used to synthesis Urolithin M7[1]. 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde is a potent tyrosinase inhibitor from three East African medicinal plants, Mondia whitei, Rhus vulgaris Meikle, and Sclerocarya caffra Sond[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Tyrosinase[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 271.5±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 41-43 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C8H8O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 152.15 |
| Flash Point | 112.1±15.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 152.047348 |
| PSA | 46.53000 |
| LogP | 1.79 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.588 |
| InChIKey | WZUODJNEIXSNEU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | COc1ccc(C=O)c(O)c1 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATAMUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | BZ2810000 |
| HS Code | 29124900 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2912499000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2912499000. other aldehyde-ethers, aldehyde-phenols and aldehydes with other oxygen function. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:9.0%. . MFN tariff:5.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
3D-QSAR and molecular docking studies of benzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone, benzaldehyde, benzoic acid, and their derivatives as phenoloxidase inhibitors.
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 15 , 2006-15, (2007) Phenoloxidase (PO), also known as tyrosinase, is a key enzyme in insect development, responsible for catalyzing the hydroxylation of tyrosine into o-diphenols and the oxidation of o-diphenols into o-q... |
|
|
Flavoring extracts of Hemidesmus indicus roots and Vanilla planifolia pods exhibit in vitro acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activities.
Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 68(3) , 247-53, (2013) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) are important for treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other neurological disorders. Search for potent and safe AChEIs from plant sources still continues. In t... |
|
|
Inhibition of Cancer Cell Proliferation and Antiradical Effects of Decoction, Hydroalcoholic Extract, and Principal Constituents of Hemidesmus indicus R. Br.
Phytother Res. 29 , 857-63, (2015) Indian Sarsaparilla (Hemidesmus indicus R. Br.) is widely used in Indian traditional medicine. In the present work, we explored the effects of decoction, traditional Ayurvedic preparation, and hydroal... |
| o-Hydroxy-p-methoxybenzaldehyde |
| VHR BQ DO1 |
| 2-HO-4-MeO-C6H3CHO |
| 2-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde |
| 4-Methoxysalicylaldehyde |
| 4-Methoxysalicyaldehyde |
| Benzaldehyde,2-hydroxy-4-methoxy |
| 2-Hydroxy-p-anisaldehyde |
| p-Anisaldehyde,2-hydroxy |
| 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy benzaldehyde |
| 4-methoxy-salicylaldehyde |
| Salicylaldehyde,4-methoxy |
| EINECS 211-604-0 |
| 4-methoxy-2-hydroxybenzaldehyde |
| MFCD00003327 |
 CAS#:77-78-1
CAS#:77-78-1 CAS#:95-01-2
CAS#:95-01-2 CAS#:613-45-6
CAS#:613-45-6 CAS#:50-00-0
CAS#:50-00-0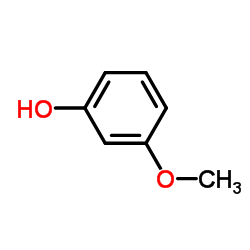 CAS#:150-19-6
CAS#:150-19-6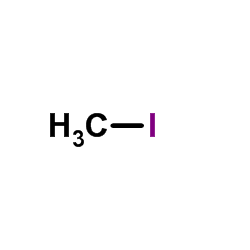 CAS#:74-88-4
CAS#:74-88-4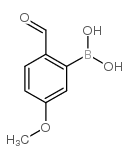 CAS#:40138-18-9
CAS#:40138-18-9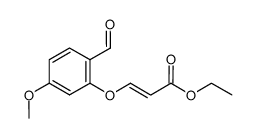 CAS#:954374-77-7
CAS#:954374-77-7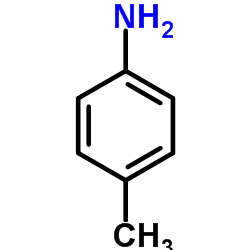 CAS#:106-49-0
CAS#:106-49-0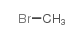 CAS#:74-83-9
CAS#:74-83-9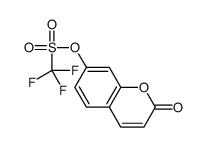 CAS#:108530-10-5
CAS#:108530-10-5 CAS#:107811-48-3
CAS#:107811-48-3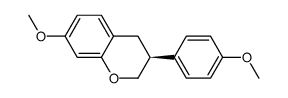 CAS#:3722-56-3
CAS#:3722-56-3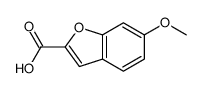 CAS#:50551-61-6
CAS#:50551-61-6 CAS#:39835-11-5
CAS#:39835-11-5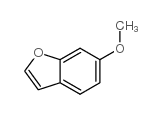 CAS#:50551-63-8
CAS#:50551-63-8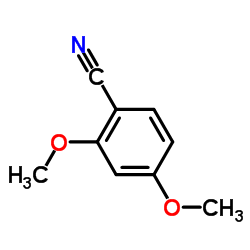 CAS#:4107-65-7
CAS#:4107-65-7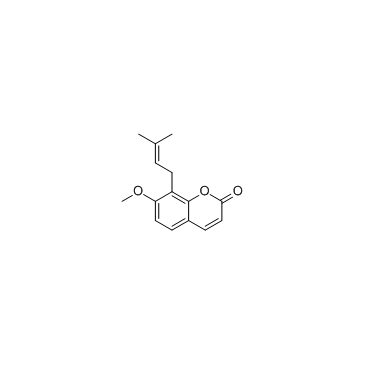 CAS#:484-12-8
CAS#:484-12-8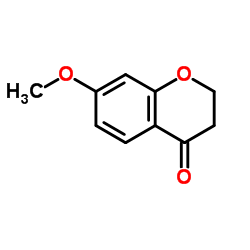 CAS#:42327-52-6
CAS#:42327-52-6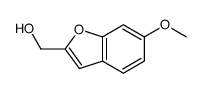 CAS#:208842-22-2
CAS#:208842-22-2
