Substrate specificity in thiamin diphosphate-dependent decarboxylases.
Forest H Andrews, Michael J McLeish
Index: Bioorg. Chem. 43 , 26-36, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Thiamin diphosphate (ThDP) is the biologically active form of vitamin B(1), and ThDP-dependent enzymes are found in all forms of life. The catalytic mechanism of this family requires the formation of a common intermediate, the 2α-carbanion-enamine, regardless of whether the enzyme is involved in C-C bond formation or breakdown, or even formation of C-N, C-O and C-S bonds. This demands that the enzymes must screen substrates prior to, and/or after, formation of the common intermediate. This review is focused on the group for which the second step is the protonation of the 2α-carbanion, i.e., the ThDP-dependent decarboxylases. Based on kinetic data, sequence/structure alignments and mutagenesis studies the factors involved in substrate specificity have been identified.Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
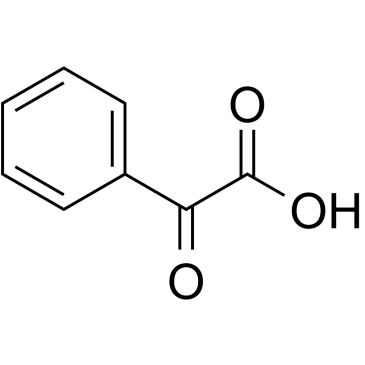 |
Phenylglyoxylic acid
CAS:611-73-4 |
C8H6O3 |
|
Development of a multi-residue method in a fetal matrix: ana...
2014-12-01 [Anal. Bioanal. Chem 406(30) , 7785-97, (2014)] |
|
Development of liquid chromatography methods coupled to mass...
2015-06-01 [Talanta 138 , 231-9, (2015)] |
|
Copper/alpha-ketocarboxylate chemistry with supporting peral...
2010-04-05 [Inorg. Chem. 49(7) , 3531-9, (2010)] |
|
Simultaneous determination of aromatic acid metabolites of s...
2012-06-01 [J. Anal. Toxicol. 36(5) , 312-8, (2012)] |
|
DNA damage and susceptibility assessment in industrial worke...
2012-01-01 [J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 75(13-15) , 735-46, (2012)] |