Chronic sinusitis in children with respiratory allergy: the role of antimicrobials.
G S Rachelefsky, R M Katz, S C Siegel
Index: J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 69(4) , 382-7, (1982)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
We evaluated the role of antimicrobials in the treatment of chronic maxillary sinusitis in children with respiratory allergy. Night and day cough, nasal obstruction, rhinorrhea, postnasal seen. Eighty-four children were treated in a double-blind manner with either amoxicillin, erythromycin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, or an antihistamine decongestant (carbinoxamine maleate-pseudoephedrine HCl). Radiographic and clinical responses were best with amoxicillin, but trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole was an adequate alternative. This study demonstrates that allergic children with chronic sinusitis with associated chronic respiratory symptoms are likely to respond clinically and radiologically with antimicrobial treatment.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
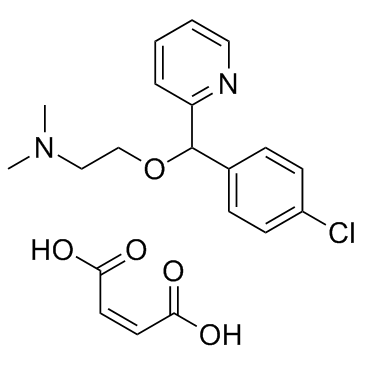 |
Carbinoxamine maleate salt
CAS:3505-38-2 |
C20H23ClN2O5 |
|
LC for analysis of two sustained-release mixtures containing...
2010-07-01 [J. Chromatogr. Sci. 48(6) , 507-12, (2010)] |
|
A comparative randomized double-blind clinical trial of hexa...
1987-06-01 [Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol. 25(6) , 310-2, (1987)] |
|
Cold-syrup induced movement disorder.
2001-06-01 [Pediatr. Emerg. Care 17(3) , 191-2, (2001)] |
|
[Serous otitis media. Comparative study of carbinoxamine- ps...
1997-01-01 [Rev. Alerg. Mex. 44(3) , 70-3, (1997)] |
|
[The efficacy of rinopront for the treatment of acute and ch...
2012-01-01 [Vestn. Otorinolaringol. (3) , 88-91, (2012)] |