The effect of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on IgE-mediated histamine release from human lung mast cells and basophils.
S E Lavens-Phillips, E H Mockford, J A Warner
Index: Inflamm. Res. 47(3) , 137-43, (1998)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
To investigate the role of tyrosine kinases (TK) in IgE-mediated signal transduction in human lung mast cells (HLMC) and basophils.Peripheral blood basophils (n > or = 4) and human lung mast cells (n > or = 6).Cells were preincubated with TK inhibitor for 15 min at 37 degrees C, before the addition of anti-IgE.Histamine release (HR) was assayed using a fluorimetric technique. Results were compared using nonparametric statistics.Piceatannol and ST638 significantly (p < or = 0.05) inhibited anti-IgE induced HR from HLMCs and basophils whilst lavendustin C had no effect in either cell type. Herbimycin A also significantly (p < or = 0.05) inhibited anti-IgE induced HR from both cell types, an effect which was dose dependent but did require a 16 h preincubation with drug.In summary, HLMCs and basophils exhibit distinct inhibitory profiles in the presence of various inhibitors of TK.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
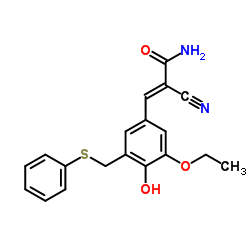 |
ST638
CAS:107761-24-0 |
C19H18N2O3S |
|
The effect of a naphthalene derivative, TEI-6472, on histami...
1995-05-01 [Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 17(5) , 433-41, (1995)] |
|
Inhibition of fast sodium current in rabbit ventricular myoc...
2003-07-01 [Pflugers Arch. 446(4) , 485-91, (2003)] |
|
Involvement of phosphatidic acid in both degranulation and o...
2003-01-01 [Cell Physiol. Biochem. 13(3) , 165-72, (2003)] |
|
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor markedly suppresses the developmen...
1997-04-01 [J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 29(4) , 536-45, (1997)] |
|
Tyrosine and calcium/calmodulin kinases are common signaling...
1999-01-01 [Life Sci. 65(20) , 2135-42, (1999)] |