Hepatic protein arylation, glutathione depletion, and metabolite profiles of acetaminophen and a non-hepatotoxic regioisomer, 3'-hydroxyacetanilide, in the mouse.
M S Rashed, T G Myers, S D Nelson
Index: Drug Metab. Dispos. 18(5) , 765-70, (1990)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The metabolism and disposition of acetaminophen (APAP) and a non-hepatotoxic regioisomer, 3'-hydroxyacetanilide (AMAP), were investigated in the mouse using 14C-labeled analogues. Covalent binding of metabolites of both compounds was observed on the order of 1 nmol/mg tissue protein. AMAP binding was much higher than that of APAP at 1 hr, but by 24 hr, AMAP binding was significantly lower than that of APAP. APAP binding peaked at 3 hr and did not decrease significantly thereafter. Despite the high early levels of covalent binding, AMAP was not as effective in causing glutathione depletion as was APAP. This was reflected in the urinary metabolite profiles of the two compounds. Approximately twice as much APAP was cleared through thioether conjugation compared to AMAP, based on an analysis of urinary metabolites. These results and results of other studies suggest that electrophilic metabolites of AMAP are more reactive than those of APAP, and do not diffuse as far from their site of formation, which may spare some critical target proteins from damage.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
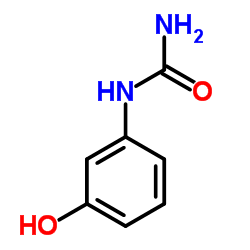 |
1-(3-Hydroxyphenyl)urea
CAS:621-42-1 |
C8H9NO2 |
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the predicti...
2010-07-19 [Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010)] |
|
A predictive ligand-based Bayesian model for human drug-indu...
2010-12-01 [Drug Metab. Dispos. 38 , 2302-8, (2010)] |
|
Cellular apoptosis and cytotoxicity of phenolic compounds: a...
2005-11-17 [J. Med. Chem. 48 , 7234-42, (2005)] |
|
Favipiravir inhibits acetaminophen sulfate formation but min...
2015-11-01 [Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 80 , 1076-85, (2015)] |
|
Use of a systems model of drug-induced liver injury (DILIsym...
2014-04-21 [Toxicol. Lett. 226(2) , 163-72, (2014)] |