Asymmetric hydrogenation using chiral Rh complexes immobilised with a new ion-exchange strategy.
William P Hems, Paul McMorn, Stewart Riddel, Simon Watson, Frederich E Hancock, Graham J Hutchings
Index: Org. Biomol. Chem. 3(8) , 1547-50, (2005)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Rh diphosphine complexes using DuPhos and JosiPhos as chiral ligands have been immobilised by ion exchange into the mesoporous material MCM-41. When used as catalysts for the enantioselective hydrogenation of dimethyl itaconate and methyl-2-acetamidoacrylate, these heterogeneous catalysts give catalytic performance in terms of yield and enantioselection that are comparable to the corresponding homogeneous catalysts. Furthermore, the heterogeneous catalysts can be readily recovered and reused without loss of catalyst performance. A second immobilisation strategy is described in which [Rh(COD)2]+BF4- is initially immobilised by ion exchange and subsequently modified by the chiral diphosphine and this give comparable catalyst performance. This immobilisation strategy opens up the possibility of easy ligand-screening for parallel synthesis and libraries.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
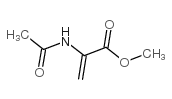 |
Methyl 2-acetamidoacrylate
CAS:35356-70-8 |
C6H9NO3 |
|
The ethyl pyruvate analogues, diethyl oxaloproprionate, 2-ac...
2005-11-25 [Biochem. Pharmacol. 70(11) , 1579-92, (2005)] |
|
Methyl-2-acetamidoacrylate, an ethyl pyruvate analog, decrea...
2008-12-01 [Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 295(6) , F1825-35, (2008)] |
|
Orthogonal synthesis of indolines and isoquinolines via aryn...
2008-02-06 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130(5) , 1558-9, (2008)] |
|
Enantioselective synthesis of tryptophan derivatives by a ta...
2012-03-21 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134(11) , 5131-7, (2012)] |
|
Extended para-hydrogenation monitored by NMR spectroscopy.
2011-01-21 [Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 47(3) , 958-60, (2011)] |