Phosphate deprivation is associated with high resistance to latamoxef of gel-entrapped, sessile-like Escherichia coli cells.
Sébastien Vilain, Pascal Cosette, Guy-Alain Junter, Thierry Jouenne
Index: J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 49(2) , 315-20, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Viable Escherichia coli cells were entrapped in agar gel layers and incubated in a phosphate-limited glucose medium. Immobilized bacteria displayed enhanced alkaline phosphatase activity and overexpressed the outer membrane protein PhoE as compared with free-floating organisms. These observations highlighted the existence of high phosphate deprivation within biofilm-like structures. In addition, the antimicrobial efficacy of latamoxef against immobilized bacteria was partly recovered in the presence of a high phosphate concentration. From these data, a possible role of phosphate deprivation in the high resistance of sessile-like organisms to antibiotics may be considered.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
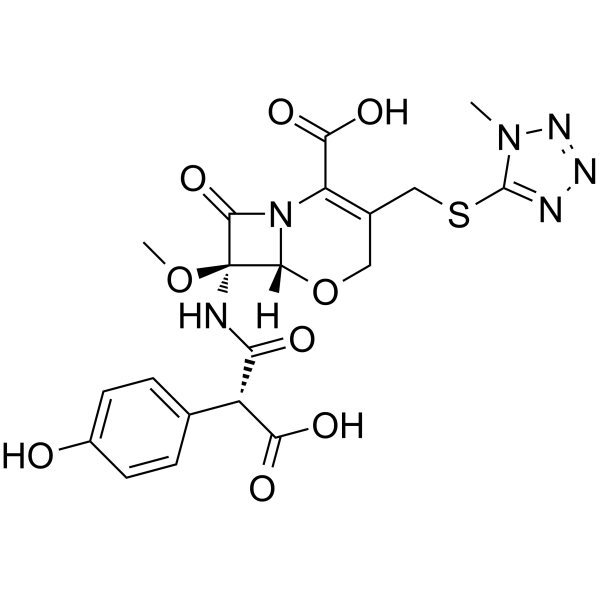 |
Latamoxef
CAS:64952-97-2 |
C20H20N6O9S |
|
A potential substrate binding conformation of β-lactams and ...
2012-10-01 [Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 56(10) , 5157-63, (2012)] |
|
Comparison of cefoxitin and moxalactam 30 microg disc diffus...
2007-04-01 [J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 59(4) , 763-6, (2007)] |
|
Subclinical syphilitic hepatitis, which was markedly worsene...
1999-06-01 [Am. J. Gastroenterol. 94(6) , 1694-6, (1999)] |
|
Inhibition of AmpC beta-lactamase through a destabilizing in...
2001-07-10 [Biochemistry 40(27) , 7992-9, (2001)] |
|
A theoretical study on the substrate deacylation mechanism o...
2005-08-25 [J. Phys. Chem. B 109(33) , 16153-60, (2005)] |