Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry
1998-07-01
ATP-dependent inactivation of Escherichia coli gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase by L-glutamic acid gamma-monohydroxamate.
M Katoh, J Hiratake, J Oda
Index: Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 62 , 1455-1457, (1998)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Incubation of Escherichia coli gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase with L-glutamic acid gamma-monohydroxamate and ATP caused slow but irreversible inhibition of the enzyme, and more than 90% activity was lost in three days. The enzyme was not inactivated when ATP was absent or L-aspartic acid beta-monohydroxamate was substituted for L-glutamic acid gamma-monohydroxamate, suggesting that the inactivation process reflected a mechanism-based reaction of L-glutamic acid gamma-monohydroxamate and ATP.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
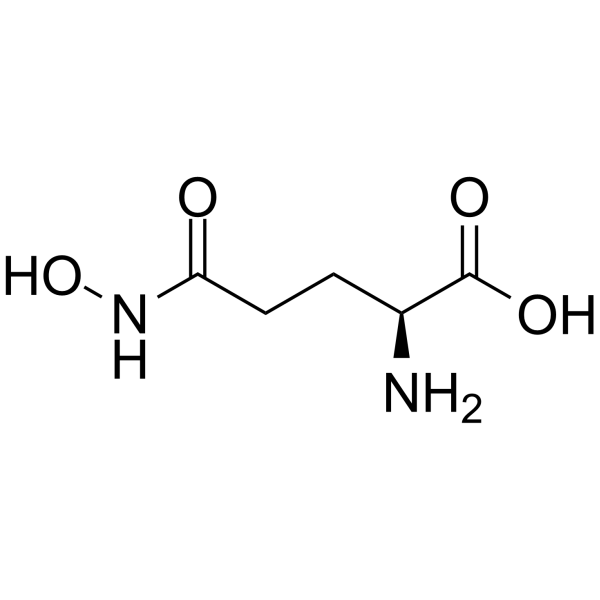 |
L-GlutaMic acid γ-MonohydroxaMate
CAS:1955-67-5 |
C5H10N2O4 |
Related Articles:
More...
|
Cell differentiation of Proteus mirabilis is initiated by gl...
1993-04-01 [Mol. Microbiol. 8(1) , 53-60, (1993)] |
|
Alternative substrates for wild-type and L109A E. coli CTP s...
2004-11-01 [Eur. J. Biochem. 271(21) , 4204-12, (2004)] |
|
Effect of epidermal growth factor on glutamine metabolic enz...
1997-01-01 [Nutrition 13(7-8) , 652-5, (1997)] |
|
Selective cytotoxicity of L-glutamic acid gamma-monohydroxam...
1993-01-01 [Anticancer Res. 13(5A) , 1393-8, (1993)] |
|
A sensitive method for the assay of glutamine synthetase.
1990-03-01 [Neurochem. Res. 15(3) , 301-5, (1990)] |