| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
KARAYA GUM
CAS:9000-36-6 |
|
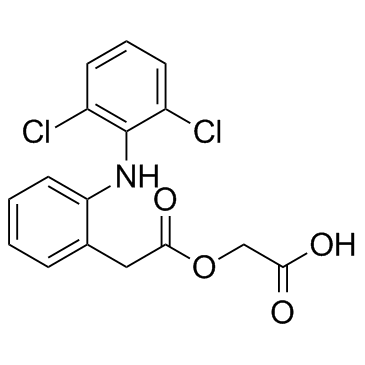 |
Aceclofenac
CAS:89796-99-6 |