Diphenyldisulfide inhibits indomethacin-induced ulcerogenesis in rats.
J M Young, A J Tomolonis
Index: Agents Actions 21(3-4) , 314-5, (1987)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Indomethacin was administered subcutaneously to rats, 4 mg/kg/day for 4 consecutive days in order to produce erosions of the small intestine which were scored at necropsy on day 5. Orally administered phenidone (up to 250 mg/kg/day), a mixed cycloocygenase-lipoxygenase inhibitor, failed to produce intestinal erosions, but tended to exacerbate indomethacin-induced erosions. A 5-LO inhibitor, diphenyldisulfide, provided significant protection at 10-100 mg/kg when given orally to indomethacin-treated rats. Sulfasalazine, auranofin and cyproheptadine, but not cimetidine, also protected, suggesting a role for mast cell activation and leukotriene generation in indomethacin-induced ulcerogenesis.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
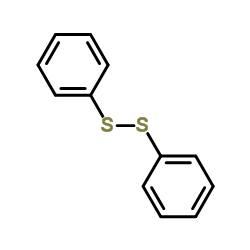 |
Diphenyl disulfide
CAS:882-33-7 |
C12H10S2 |
|
Targeting the fatty acid biosynthesis enzyme, beta-ketoacyl-...
2009-02-26 [J. Med. Chem. 52 , 952-63, (2009)] |
|
The fate of diphenyl sulphide, diphenyl sulphoxide and diphe...
2000-01-01 [Drug Metabol. Drug Interact. 16(3) , 191-206, (2000)] |
|
Functional groups and sulfur K-edge XANES spectra: divalent ...
2010-09-09 [J. Phys. Chem. A 114(35) , 9523-8, (2010)] |
|
Reductive addition of the benzenethiyl radical to alkynes by...
2009-08-06 [Org. Lett. 11(15) , 3298-301, (2009)] |
|
Molecular modeling and enzyme kinetics indicate a novel mech...
1987-01-01 [Adv. Prostaglandin. Thromboxane. Leukot. Res. 17A , 69-74, (1987)] |