Organic Letters
2006-12-07
Curtius rearrangement of aromatic carboxylic acids to access protected anilines and aromatic ureas.
Hélène Lebel, Olivier Leogane
Index: Org. Lett. 8 , 5717, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The reaction of a chloroformate or di-tert-butyl dicarbonate and sodium azide with an aromatic carboxylic acid produces the corresponding acyl azide, presumably through the formation of an azidoformate. The acyl azide undergoes a Curtius rearrangement to form an isocyanate derivative which is trapped either by an alkoxide or by an amine to form the aromatic carbamate or urea. The reaction conditions are compatible with a variety of functional groups and allow the synthesis of a number of aniline derivatives containing alkyl, halide, nitro, ketone, ether, and thioether substituents. [reaction: see text]
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
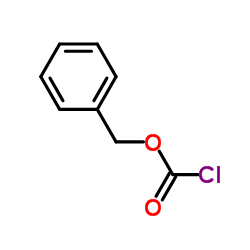 |
Benzyl chloroformate
CAS:501-53-1 |
C8H7ClO2 |
Related Articles:
More...
|
Polymeric micelles for pH-responsive delivery of cisplatin.
2014-08-01 [J. Drug Target. 22(7) , 629-37, (2014)] |
|
Ames Salmonella/mammalian-microsome testing of peptides and ...
1986-01-01 [Mutat. Res. 170(1-2) , 23-9, (1986)] |
|
Untargeted metabolomics in doping control: detection of new ...
2015-08-18 [Anal. Chem. 87 , 8373-80, (2015)] |
|
Synthesis, colon-targeted studies and pharmacological evalua...
2016-01-27 [Eur. J. Med. Chem. 108 , 486-94, (2016)] |
|
Controlled release kinetics of p-aminosalicylic acid from bi...
2016-01-15 [Acta Biomater. 30 , 168-76, (2015)] |