Tumor-targeting of EGFR inhibitors by hypoxia-mediated activation.
Claudia Karnthaler-Benbakka, Diana Groza, Kushtrim Kryeziu, Verena Pichler, Alexander Roller, Walter Berger, Petra Heffeter, Christian R Kowol
Index: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 53(47) , 12930-5, (2014)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The development of receptor tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKIs) was a major step forward in cancer treatment. However, the therapy with TKIs is limited by strong side effects and drug resistance. The aim of this study was the design of novel epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors that are specifically activated in malignant tissue. Thus, a Co(III) -based prodrug strategy for the targeted release of an EGFR inhibitor triggered by hypoxia in the solid tumor was used. New inhibitors with chelating moieties were prepared and tested for their EGFR-inhibitory potential. The most promising candidate was coupled to Co(III) and the biological activity tested in cell culture. Indeed, hypoxic activation and subsequent EGFR inhibition was proven. Finally, the compound was tested in vivo, also revealing potent anticancer activity. © 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
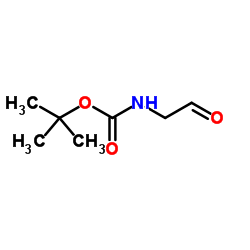 |
2-Methyl-2-propanyl (2-oxoethyl)carbamate
CAS:89711-08-0 |
C7H13NO3 |
|
Synthesis of fused heteroarylprolines and pyrrolopyrroles.
2004-07-09 [J. Org. Chem. 69 , 4656-4662, (2004)] |
|
Single cell imaging of Bruton's tyrosine kinase using an irr...
2014-01-01 [Sci. Rep. 4 , 4782, (2014)] |
|
Efficient total synthesis of (+)-negamycin, a potential chem...
2008-05-28 [Chem. Commun. (Camb.) (20) , 2379-81, (2008)] |
|
Mild organocatalytic alpha-methylenation of aldehydes.
2006-03-17 [J. Org. Chem. 71 , 2538, (2006)] |
|
[J. Org. Chem. 70 , 10869, (2005)] |