| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
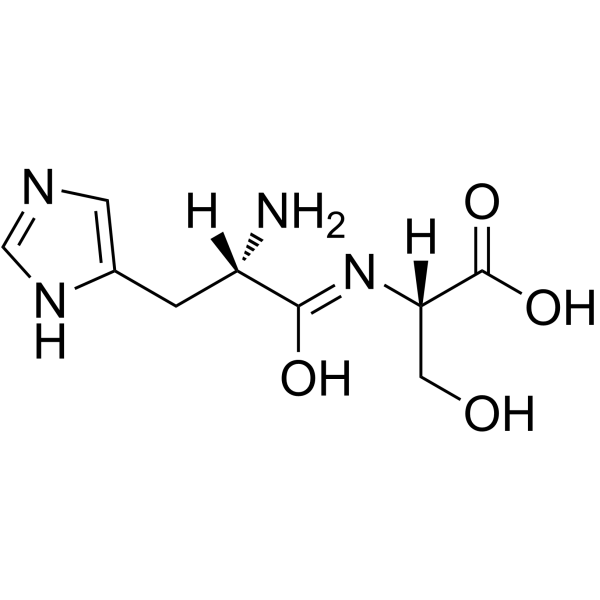 |
H-His-Ser-OH
CAS:21438-60-8 |
|
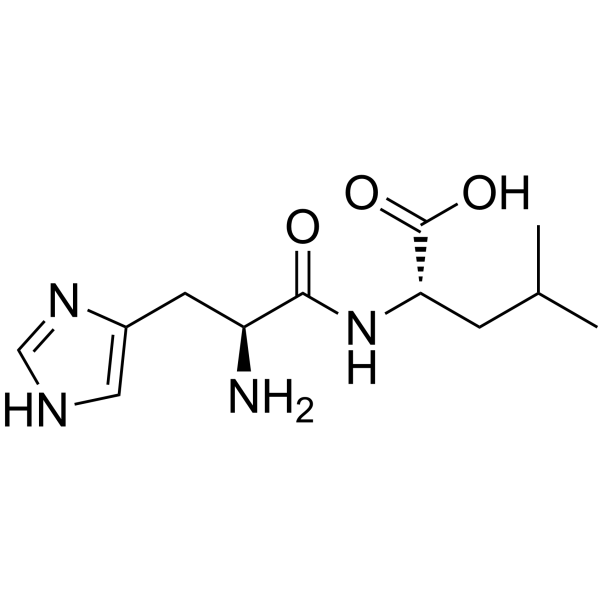 |
H-His-Leu-OH
CAS:7763-65-7 |