H-His-Ser-OH
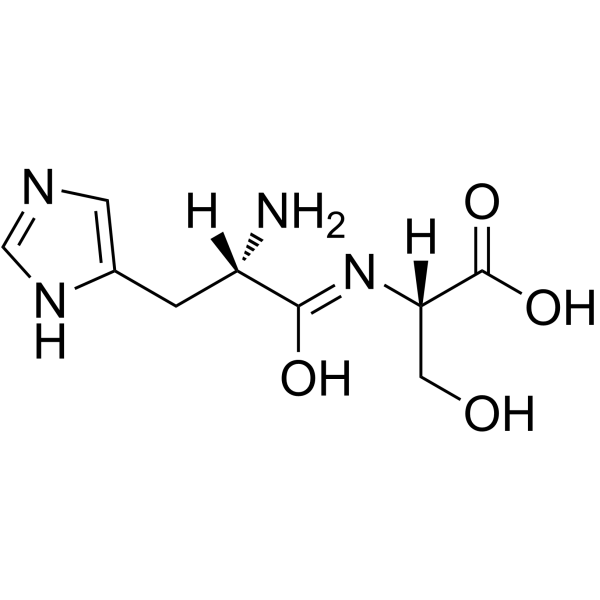
H-His-Ser-OH structure
|
Common Name | H-His-Ser-OH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 21438-60-8 | Molecular Weight | 242.23200 | |
| Density | 1.492 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 737.6ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H14N4O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 399.9ºC | |
|
Ternary nickel(II) complexes as hydrolytic DNA-cleavage agents.
Chem. Biodivers. 3 , 231-244, (2006) A series of small model complexes made from Ni(II) and the ligands ethylenediamine (en), histamine (hist), and histidylleucine (HisLeu) were prepared and studied as potential hydrolytic DNA-cleavage agents. The stability constants and species-distribution cur... |
|
|
Ternary zinc(II)-dipeptide complexes for the hydrolytic cleavage of DNA at physiological pH.
Chem. Biodivers. 2 , 672-683, (2005) A series of Zn(II) complexes with cysteinylglycine (CysGly) and histidylserine (HisSer), and of CysGly and histidylphenylalanine (HisPhe) were investigated. Complex stabilities were determined potentiometrically, and binding geometries were probed by means of... |
|
|
L-histidyl-L-serine 3.7-hydrate: water channels in the crystal structure of a polar dipeptide.
Acta Crystallogr. C 66 , o531-534, (2010) Dipeptides may form nanotubular structures with pore diameters in the range 3.2-10 Å. These compounds normally contain at least one and usually two hydrophobic residues, but L-His-L-Ser hydrate, C(9)H(14)N(4)O(4)·3.7H(2)O, with two hydrophilic residues, forms... |
|
|
Novel peptide-based copper(II) complexes for total hydrolytic cleavage of DNA.
Chem. Biodivers. 2 , 1338-1350, (2005) Stable Cu(II) complexes with histamine- and histidine-containing dipeptides histidylserine and histidylphenylalanine have been developed. Their interaction in solution has been investigated, and the stability of their complexes was determined. The nature of b... |
|
|
Copper(II) complexes containing N,N-donor ligands and dipeptides act as hydrolytic DNA-cleavage agents.
Chem. Biodivers. 1 , 839-853, (2004) Copper(II) complexes are known to play a significant role in both naturally occurring biological systems and pharmaceutical agents. Recently, Cu(II) complexes have gained importance in DNA cleavage essential for the development of anticancer drugs and chemoth... |