Diversity of fungi in creosote-treated crosstie wastes and their resistance to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Min-Ji Kim, Hwanhwi Lee, Yong-Seok Choi, Gyu-Hyeok Kim, Na-Yoon Huh, Sangjoon Lee, Young Woon Lim, Sung-Suk Lee, Jae-Jin Kim
Index: Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 97(4) , 377-87, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
This study was conducted to generate information regarding the diversity of fungi inhabiting creosote-treated wood in a storage yard for crosstie wastes in Gwangmyeong, Korea. Additionally, the resistance to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) of indigenous fungi that mainly occupy creosote-treated wood was evaluated. We isolated fungi from the surface and inner area of crosstie wastes and identified them using a combination of traditional methods and molecular techniques. Overall, 179 isolates including 47 different species were isolated from 240 sampling sites. The identified fungal species included 23 ascomycetes, 19 basidiomycetes, and 5 zygomycetes. Three species, Alternaria alternata, Irpex lacteus, and Rhizomucor variabilis, were the most frequently isolated ascomycetes, basidiomycetes, and zygomycetes, respectively. The results of this study showed that there was a large difference in the fungal diversity between the surface and the inner area. Additionally, zygomycetes and ascomycetes were found to have a greater tolerance to PAHs than basidiomycetes. However, two basidiomycetes, Heterobasidion annosum and Schizophyllum commune, showed very high resistance to PAHs, even in response to the highest concentration (1,000 ppm), which indicates that these species may play a role in the degradation of PAHs.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
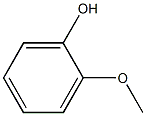 |
Creosote wood
CAS:8021-39-4 |
C7H8O2 |
|
Microbial populations related to PAH biodegradation in an ag...
2009-09-01 [Biodegradation 20(5) , 593-601, (2009)] |
|
Degradation of PAH in a creosote-contaminated soil. A compar...
2010-01-01 [Int. J. Phytoremediation 12(1) , 54-66, (2010)] |
|
Self-sustaining smoldering combustion for NAPL remediation: ...
2011-04-01 [Environ. Sci. Technol. 45(7) , 2980-6, (2011)] |
|
An integrated assessment of sediment remediation in a midwes...
2013-03-01 [Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 32(3) , 653-61, (2013)] |
|
Functional genes reveal the intrinsic PAH biodegradation pot...
2009-08-01 [Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 84(1) , 169-82, (2009)] |