Creosote wood
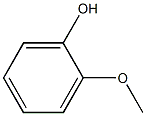
Creosote wood structure
|
Common Name | Creosote wood | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 8021-39-4 | Molecular Weight | 124.13722 | |
| Density | 1.09 g/mL at 20 °C | Boiling Point | 200-220 °C(lit.) | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H8O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 74 °C | |
| Symbol |




GHS05, GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | Creosote wood |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.09 g/mL at 20 °C |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 200-220 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7H8O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 124.13722 |
| Flash Point | 74 °C |
| Symbol |




GHS05, GHS06, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 + H311-H314-H332-H335-H341-H373-H411 |
| Precautionary Statements | Missing Phrase - N15.00950417-P260-P280-P303 + P361 + P353-P304 + P340 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;Goggles;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | T,C |
| Risk Phrases | 23/24/25-34-48/20/21/22-68-52/53-37 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36/37/39-45-61 |
| RIDADR | UN 2922 8/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | GO5870000 |
|
Microbial populations related to PAH biodegradation in an aged biostimulated creosote-contaminated soil.
Biodegradation 20(5) , 593-601, (2009) A previous bioremediation survey on a creosote-contaminated soil showed that aeration and optimal humidity promoted depletion of three-ringed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), but residual conc... |
|
|
Degradation of PAH in a creosote-contaminated soil. A comparison between the effects of willows (Salix viminalis), wheat straw and a nonionic surfactant.
Int. J. Phytoremediation 12(1) , 54-66, (2010) The degradation of polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in an aged creosote-contaminated soil in the presence of Salix viminalis was investigated in a greenhouse experiment. Phenanthrene and pyrene were de... |
|
|
Self-sustaining smoldering combustion for NAPL remediation: laboratory evaluation of process sensitivity to key parameters.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 45(7) , 2980-6, (2011) Smoldering combustion has been introduced recently as a potential remediation strategy for soil contaminated by nonaqueous phase liquids (NAPLs). Published proof-of-concept experiments demonstrated th... |
| EINECS 232-419-1 |