Protective effect of aripiprazole against glutamate cytotoxicity in dopaminergic neurons of rat mesencephalic cultures.
Takaaki Matsuo, Yasuhiko Izumi, Toshiaki Kume, Yuki Takada-Takatori, Hideyuki Sawada, Akinori Akaike
Index: Neurosci. Lett. 481(2) , 78-81, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Aripiprazole, a dopamine D(2) receptor partial agonist, is used to treat schizophrenia. Although aripiprazole has been reported to protect non-dopaminergic neurons, its effect on dopaminergic neurons has yet to be investigated. In the present study, we examined whether aripiprazole protected dopaminergic neurons against glutamate-induced cytotoxicity in rat mesencephalic cultures. Pretreatment with aripiprazole protected dopaminergic neurons in a concentration-dependent manner. The neuroprotective effect was not attenuated by sulpiride, a dopamine D(2) receptor antagonist, suggesting that the effect is independent of dopamine D(2) receptors. Aripiprazole reduced intracellular dopamine content in a concentration-dependent manner. In addition, its neuroprotective effect was partially inhibited when dopamine was added. These results suggest that aripiprazole protects dopaminergic neurons against glutamate cytotoxicity partly by reducing intracellular dopamine content.Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
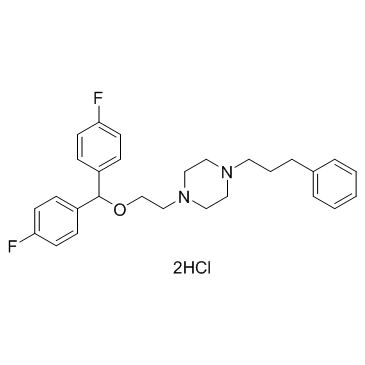 |
Vanoxerine dihydrochloride
CAS:67469-78-7 |
C28H34Cl2F2N2O |
|
Serotonin at the level of the amygdala and orbitofrontal cor...
2012-02-01 [Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. , 1-15, (2011)] |
|
Dopamine uptake inhibitors but not dopamine releasers induce...
2010-10-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 335(1) , 124-32, (2010)] |
|
Differential effects of dopamine transporter inhibitors in t...
2013-02-01 [Psychopharmacology 225(3) , 661-74, (2013)] |
|
Dopamine transporter-dependent and -independent striatal bin...
2010-12-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 335(3) , 703-14, (2010)] |
|
Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder-derived coding vari...
2012-04-18 [J. Neurosci. 32(16) , 5385-97, (2012)] |