Journal of the American Chemical Society
2004-09-29
Degradation of N-acetyl tryptophan by low-energy (<12 eV) electrons.
Hassan Abdoul-Carime, Sascha Gohlke, Eugen Illenberger
Index: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126(38) , 12158-61, (2004)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Secondary low-energy electrons are abundantly created during the early moments following the deposition of energy by radiation into cells. Here we show the ability of slow (<12 eV) electrons to effectively decompose gas-phase N-acetyl tryptophan (NAT) which can model a simple protein. The fragmentation of NAT, initiated via a resonant electron-molecule interaction exclusively at the peptide bridge, produces a large variety of negative species. The present findings contribute to the molecular description of the initial step in the radiation-induced damage.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
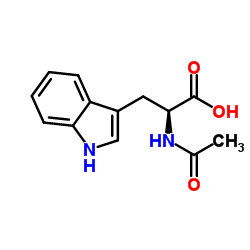 |
Acetyl-L-tryptophan
CAS:1218-34-4 |
C13H14N2O3 |
Related Articles:
More...
|
Transport and signaling via the amino acid binding site of t...
2009-01-01 [Nat. Chem. Biol. 5 , 45-52, (2009)] |
|
Electron transfer from aromatic amino acids to triplet quino...
2007-09-25 [J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, Biol. 88(2-3) , 83-9, (2007)] |
|
Nucleoprotein photo-cross-linking using halopyrimidine-subst...
2000-01-01 [Meth. Enzymol. 318 , 88-104, (2000)] |
|
Stabilizing mechanisms in commercial albumin preparations: o...
2004-10-01 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1702 , 9-17, (2004)] |
|
Pressure effects on tryptophan and its derivatives.
2000-03-24 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 269(3) , 681-6, (2000)] |