GC/MS comparison of the West Indian aphrodisiac "Love Stone" to the Chinese medication "chan su": bufotenine and related bufadienolides.
T L Barry, G Petzinger, S W Zito
Index: J. Forensic Sci. 41(6) , 1068-73, (1996)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The death of a 23-year-old man resulting from digoxin-like toxicity and heart failure was attributed to ingestion of a West Indian aphrodisiac known as "Love Stone." GC/MS analyses identified bufotenine, a controlled substance under both US and New York State statutes. In addition, a series of bufadienolides, namely resibufogenin, bufalin, and cinobufagin, were also identified. Bufadienolides, which are derived from toad venom or secretions, are cardiotonic steroids that cause symptoms similar to digoxin. GC/MS analyses of the Chinese medication "Chan Su," a product derived from toads, produced a highly similar elution profile and contained the same compounds as "Love Stone." The data demonstrate that the aphrodisiac was also derived from toads.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
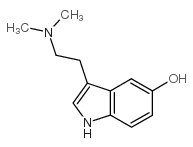 |
Bufotenine
CAS:487-93-4 |
C12H16N2O |
|
Psychedelic 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine: metabolism, ph...
2010-10-01 [Curr. Drug Metab. 11(8) , 659-66, (2010)] |
|
Isolation of N,N-dimethyl and N-methylserotonin 5-O-β-glucos...
2010-01-01 [Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 74(9) , 1951-2, (2010)] |
|
A critical review of reports of endogenous psychedelic N, N-...
2012-01-01 [Drug Test. Anal. 4(7-8) , 617-35, (2012)] |
|
Treatment of toad venom poisoning with digoxin-specific Fab ...
1996-11-01 [Chest 110(5) , 1282-8, (1996)] |
|
Sudden death associated with intravenous injection of toad e...
2009-07-01 [Forensic Sci. Int. 188(1-3) , e1-5, (2009)] |