Localized glucoprivation of hindbrain sites elicits corticosterone and glucagon secretion.
Shayne F Andrew, Thu T Dinh, Sue Ritter
Index: Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 292(5) , R1792-8, (2007)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Glucose is required for brain energy metabolism. Decerebration, aqueduct occlusion, and cannula mapping studies have established that glucose-sensing cells capable of eliciting feeding and adrenal medullary responses to glucoprivation are localized in the hindbrain. Glucoprivation also evokes corticosterone and glucagon secretion, but the location of receptors mediating these responses is unknown. To determine whether glucoreceptive sites controlling these responses are present in the hindbrain, we administered the antiglycolytic agent, 5-d-thioglucose (5TG, 24 microg in 200 nl) into brain stem sites through implanted cannulas and examined plasma concentrations of corticosterone and glucagon. Both hindbrain and hypothalamic sites were tested. Blood was collected remotely from intra-atrial catheters at 0, 30, 60, 90, 120, 180, and 240 min after 5TG or control injection. Caudal hindbrain 5TG injections potently increased circulating corticosterone and glucagon concentrations. For corticosterone, the mean peak response (maximum concentration minus time 0 concentration) elicited at positive sites (23 of 40 sites) was 391 ng/ml (SE = 16). For glucagon, the mean peak response at positive sites (27 of 40 sites) was 46 pg/ml (SE = 6). Glucoprivically evoked glucagon secretion was abolished by the ganglionic blocker, hexamethonium, but not by adrenal denervation. Six of twenty-five hypothalamic sites were positive for corticosterone secretion, yielding plasma levels of 279 +/- 23 ng/ml, but none of the hypothalamic injection sites elevated glucagon concentrations. Results demonstrate that receptor cells responsive to glucose deficit and capable of increasing corticosterone and glucagon concentrations exist within the hindbrain, thus further delineating central glucoregulatory neural circuitry.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
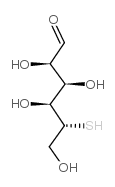 |
5-THIO-D-GLUCOSE
CAS:20408-97-3 |
C6H12O5S |
|
Thrombin mediates vagal apoptosis and dysfunction in inflamm...
2014-08-01 [J. Gastrointest. Surg. 18(8) , 1495-506, (2014)] |
|
GLUT2 in pancreatic islets: crucial target molecule in diabe...
1998-01-01 [Diabetes 47 , 50-56, (1998)] |
|
The use of fluoro- and deoxy-substrate analogs to examine bi...
1998-12-15 [Carbohydr. Res. 313(3-4) , 247-53, (1998)] |
|
Intraperitoneal CCK and fourth-intraventricular Apo AIV requ...
2014-05-01 [Endocrinology 155(5) , 1700-7, (2014)] |
|
Hypothalamus-brain stem circuitry responsible for vagal effe...
2013-08-01 [J. Neurophysiol. 91(4) , 1734-47, (2004)] |