Journal of Hepatology
2011-06-01
Direct effects of iodothyronines on excess fat storage in rat hepatocytes
Elena Grasselli, Adriana Voci, Laura Canesi, Rita De Matteis, Fernando Goglia, Federica Cioffi, Emilia Fugassa, Gabriella Gallo, Laura Vergani
Index: J. Hepatol. 54(6) , 1230-6, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Background & Aims Previous studies have demonstrated that 3,5-l-diiodothyronine (T2) is able to prevent lipid accumulation in the liver of rats fed a high-fat diet. Whether this effect is due to a direct action of T2 on the liver has not been elucidated. In this study, we investigated the ability of T2 to reduce the excess lipids in isolated hepatocytes treated with fatty acids (FFAs). The effects of T2 were compared with those elicited by 3,3′,5-l-triiodothyronine (T3).
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
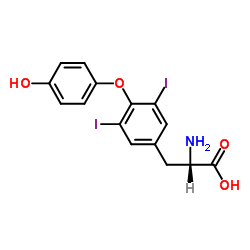 |
3,5-Diiodo-L-thyronine
CAS:1041-01-6 |
C15H13I2NO4 |
Related Articles:
More...
|
Administration of 3,5-diiodothyronine (3,5-T2) causes centra...
2014-06-01 [J. Endocrinol. 221(3) , 415-27, (2014)] |
|
In Vitro, Ex Vivo, and In Vivo Determination of Thyroid Horm...
2015-08-01 [Toxicol. Sci. 146 , 254-64, (2015)] |
|
Ion pair hollow fiber liquid-liquid-liquid microextraction c...
2014-08-22 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1356 , 23-31, (2014)] |
|
Acute effects of thyroid hormone analogs on sodium currents ...
1999-04-01 [J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 31 , 881-93, (1999)] |
|
3,5-Diiodothyronine in vivo maintains euthyroidal expression...
2007-08-01 [Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 293(2) , R877-83, (2007)] |