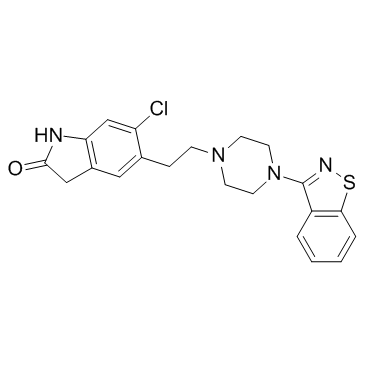
146939-27-7
| Name | ziprasidone |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
5-{2-4-(1,2-benzothiazol-3-yl)piperazin-1-ylethyl}-6-chloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one
5-{2-[4-(1,2-Benzisothiazol-3-yl)piperazin-1-yl]ethyl}-6-chloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one ziprasidonum Ziprasidone UNII-6UKA5VEJ6X 5-{2-[4-(1,2-Benzothiazol-3-yl)piperazin-1-yl]ethyl}-6-chloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one ziprasidona EINECS 203-794-9 5-{2-[4-(1,2-Benzisothiazol-3-yl)piperazin-1-yl]ethyl}-6-chlor-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-on Zipwell MFCD00866661 5-{2-[4-(1,2-Benzothiazol-3-yl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl}-6-chloro-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one ziprazidone Ziprasidone [INN:BAN] Geodon Zeldox 5-[2-[4-(1,2-benzothiazol-3-yl)piperazin-1-yl]ethyl]-6-chloro-1,3-dihydroindol-2-one |
| Description | Ziprasidone(CP88059) is a combined 5-HT (serotonin) and dopamine receptor antagonist which exhibits potent effects of antipsychotic activity.IC50 value:Target: 5-HT receptor; Dopamine receptorZiprasidone possesses an in vitro 5-HT2A/dopamine D2 receptor affinity ratio higher than any clinically available antipsychotic agent. In vivo, ziprasidone antagonizes 5-HT2A receptor-induced head twitch with 6-fold higher potency than for blockade of d-amphetamine-induced hyperactivity, a measure of central dopamine D2 receptor antagonism. Ziprasidone also has high affinity for the 5-HT1A, 5-HT1D and 5-HT2C receptor subtypes, which may further enhance its therapeutic potential [1]. Ziprasidone sulfoxide and sulfone were the major metabolites in human serum. The affinities of the sulfoxide and sulfone metabolites for 5-HT2 and D2 receptors are low with respect to ziprasidone, and are thus unlikely to contribute to its antipsychotic effects [2]. Ziprasidone was associated with significant differential adverse effects relative to placebo in BPM, BPD, and schizophrenia with no significant difference in weight gain in all 3 groups. Self-reported somnolence was increased across the 3 conditions. Subjects with BPM were more vulnerable to EPS than those with BPD or schizophrenia [3].Clinical indications: Bipolar I disorder; Bipolar disorder; Mania; SchizophreniaFDA Approved Date: February 2001 |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 554.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 213-215°C |
| Molecular Formula | C21H21ClN4OS |
| Molecular Weight | 412.94 |
| Flash Point | 289.3±30.1 °C |
| PSA | 76.71000 |
| LogP | 4.00 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.681 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS07, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H315-H360FD |
| Supplemental HS | May form explosive peroxides. |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P210-P308 + P313-P403 + P235 |
| Hazard Codes | C,N |
| Risk Phrases | R22:Harmful if swallowed. R34:Causes burns. R50/53:Very Toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment . R20/21/22:Harmful by inhalation, in contact with skin and if swallowed . |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39-S45-S60-S61 |
| RIDADR | UN 3259 8/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | JR6475000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 8 |
| HS Code | 29211980 |
| HS Code | 29211980 |
|---|