151519-02-7
| Name | (2R,3R)-3-ethyl-2-[(E,2R,3S,4R,5S)-2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylnon-7-enyl]-2,3-dihydropyran-6-one |
|---|
| Description | Pironetin is an α/β unsaturated lactone isolated from Streptomyces species. Pironetin binds to α-tubulin and is a potent inhibitor of microtubule polymerization, and has cell cycle arrest and antitumor activity[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Microtubule[1] |
| In Vitro | Pironetin (20-100 ng/mL; 24 hours; 3Y1 cells) treatment arrests the cell cycle progression at G2/M in 3Y1 cells[1]. Pironetin (1-10000 ng/mL; 3 days; HeLa, A2780 and K-NRK cells) treatment inhibits the cell proliferation. IC50 values against these cell lines are almost 10 ng/mL[1]. Cell Cycle Analysis[1] Cell Line: 3Y1 cells Concentration: 20 ng/mL, 50 ng/mL, 100 ng/mL Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Arrested the cell cycle progression at G2/M in3Y1 cells. Cell Proliferation Assay[1] Cell Line: HeLa, A2780 and K-NRK cells Concentration: 1 ng/mL, 10 ng/mL, 100 ng/mL, 1000 ng/mL and 10000 ng/mL Incubation Time: 3 days Result: Inhibited the cell proliferation. |
| In Vivo | Pironetin (0.78-6.25 mg/kg; intraperitoneal injection; daily; for 5 days; female CDF1-SLC mice) treatment shows a moderate antitumor effect, however, a severe weight loss is observed as a side effect[1]. Animal Model: Female CDF1-SLC mice (10 weeks) injected with P388 murine leukemia cells[1] Dosage: 0.78 mg/kg, 1.56 mg/kg, 3.13 mg/kg, 6.25 mg/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal injection; daily; for 5 days Result: Showed a moderate antitumor effect. |
| References |
| Density | 0.993 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 473.1ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C19H32O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 324.45500 |
| Flash Point | 160.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 324.23000 |
| PSA | 55.76000 |
| LogP | 3.49860 |
| Vapour Pressure | 6.14E-11mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.478 |
| Precursor 5 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
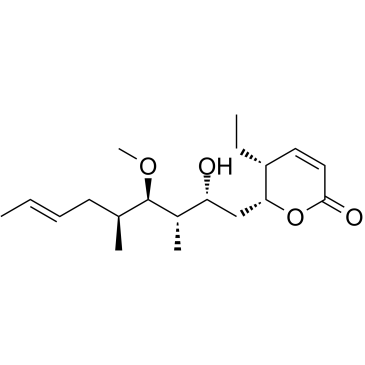
![(5R,6R,2'R,3'R,4'R,5'S)-(7'E)-9'-5-Ethyl-5,6-dihydro-6-[4'-methoxy-2'-[(methoxymethyl)oxy]-3',5'-dimethyl-7'-nonenyl]-2H-pyran-2-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/317/172603-27-9.png)
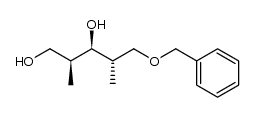
![(2R,3S,4R)-1-(Benzyloxy)-5-[(tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)oxy]-2,4-dimethyl-3-pentanol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/381/172722-41-7.png)
![(2R,3S,4R)-1-(Benzyloxy)-5-[(tert-butyldiphenylsilyl)oxy]-3-methoxy-2,4-dimethylpentane structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/252/172603-11-1.png)
