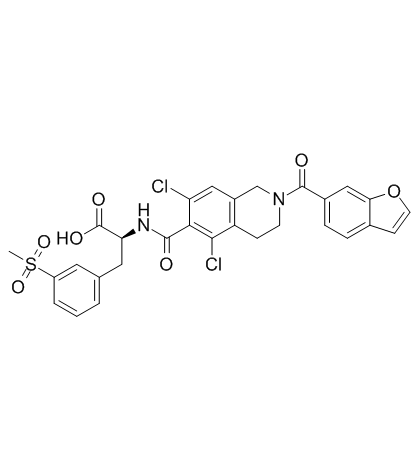
1025967-78-5
| Name | Lifitegrast |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
N-{[2-(1-Benzofuran-6-ylcarbonyl)-5,7-dichloro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6-isoquinolinyl]carbonyl}-3-(methylsulfonyl)-L-phenylalanine
Lifitegrast N-[[2-(6-Benzofuranylcarbonyl)-5,7-dichloro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6-isoquinolinyl]carbonyl]-3-(methylsulfonyl)-L-phenylalanine SAR 1118 |
| Description | Lifitegrast is an integrin lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1) antagonist; inhibits Jurkat T cell attachment to ICAM-1 with an IC50 of 2.98 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 2.98 nM (LFA-1)[1] |
| In Vitro | Lifitegrast is a novel small molecule integrin antagonist that inhibits T cell-mediated inflammation by blocking the binding of two important cell surface proteins (lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 and intercellular adhesion molecule 1), thus lessening overall inflammatory responses. Lifitegrast strongly inhibits Jurkat T cell attachment to ICAM-1 with an IC50 of 2.98 nM[1]. |
| In Vivo | Lifitegrast, has potent anti-inflammatory activity on corneal inflammation induced by antibiotic-killed P. aeruginosa and S. aureus in the presence of a silicone hydrogel lens with the optimal application being a 1% solution applied either 2 or 3 times prior. Topical application of lifitegrast to the corneal surface of healthy adults is safe and well tolerated[2]. SAR 1118 ophthalmic drops administered thrice daily deliver therapeutic levels of SAR 1118 in the retina and can alleviate the retinal complications associated with diabetes[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: The ocular pharmacokinetics of SAR 1118 are studied in rats after a single topical dose of 14C-SAR 1118 (1 mg/eye; 40 μCi; 15.5 μL). SAR 1118 concentration time profiles in plasma and ocular tissues are quantified by liquid scintillation counting (LSC). The pharmacologic activity of SAR 1118 eye drops administered thrice daily for 2 months at 1% (0.3 mg/eye/d) and 5% (1.5 mg/eye/d) is assessed in an STZ-induced diabetic rat model by determining retinal leukostasis and blood–retinal barrier breakdown[3]. Mice: The role of LFA-1 (CD11a/CD18) is examined either in CD18-/- mice, by intraperitoneal injection of anti-CD11a, or by topical application of lifitegrast. Corneal inflammation is induced by epithelial abrasion and exposure to either tobramycin-killed Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Staphylococcus aureus in the presence of a 2-mm-diameter punch from a silicone hydrogel contact lens. After 24 h, corneal thickness and haze are examined by confocal microscopy, and neutrophil recruitment to the corneal stroma is detected by immunohistochemistry[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 811.9±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C29H24Cl2N2O7S |
| Molecular Weight | 615.481 |
| Flash Point | 444.8±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 614.068115 |
| PSA | 142.37000 |
| LogP | 1.54 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.661 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |