867063-97-6
| Name | Atiratecan |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
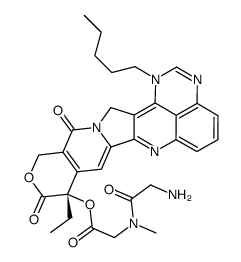
(9S)-9-Et1,2,3-Phyl-10,13-dioxo-1-pentyl-9,10,13,15-tetrahydro-1H,12H-pyrano(3'',4'':6',7')indolizino(2',1':5,6)pyrido(4,3,2-de)quinazolin-9-yl glycyl-N-methylglycinate
UNII-B0AMG37FFR |
| Description | Atiratecan (TP300) is a prodrug of camptothecin analog CH0793076 (HY-107096). Atiratecan does not inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activities. Atiratecan shows antitumor activity against both breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP)-positive and -negative xenografts in mouse xenograft models[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Atiratecan (TP300) is stable in an acidic solution but is rapidly converted to CH0793076 under physiological pH conditions such as in sera[1]. Atiratecan has antiproliferative activity against camptothecin-resistant cell lines. Atiratecan has IC50s of 9.4 nM and 1.1 nM for A2780 and A2780/SN75 cells, respectively[1]. |
| In Vivo | Atiratecan (TP300; 47 mg/kg; IV; once per week for 3 weeks) shows more than 50% of tumor growth inhibition in all nine models, regardless of the expression of BCRP[1]. Atiratecan (24 mg/kg; IV; once per week for 6 weeks) in combination with capecitabine results in synergistic eVects in the HCT116 human colon cancer and NCI-N87 human gastric cancer xenograft models and an additive eVect in the WiDr human colon cancer xenograft model which is BCRP-positive and CPT-11-insensitive[1]. The eVective dose range of Atiratecan is between 0.30 and 47 mg/kg (MTD/ED50=157). The toxic dose is 63 mg/kg for Atiratecan[1]. Animal Model: Five-week-old male athymic nude mice (CAnN.CgFoxn1nu/CrlCrlj)[1] Dosage: 47 mg/kg (the maximum tolerated dose; MTD) Administration: IV; once per week for 3 weeks Result: Showed more than 50% of tumor growth inhibition in all models, regardless of the expression of BCRP. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C31H34N6O6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 586.63800 |
| Exact Mass | 586.25400 |
| PSA | 151.64000 |
| LogP | 3.28780 |