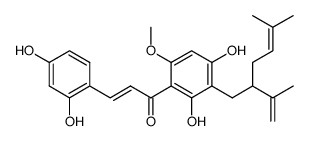
34981-25-4
| Name | Kuraridine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
6'-methoxy-2,4,2',4'-tetrahydroxy-3'-lavandulylchalcone
kuraridin kuraridine (E)-1-[2,4-Dihydroxy-3-(2-isopropenyl-5-methyl-hex-4-enyl)-6-methoxy-phenyl]-3-(2,4-dihydroxy-phenyl)-propenone |
| Description | Kuraridine is a prenylated flavonol extract from the roots of Sophora flavescens. Kuraridine an inhibitory effect on cGMP specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) and has an IC50 of 0.64 μM[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
PDE5:0.64 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Kuraridine shows potent inhibitory activity (IC50=0.64 μM) against cGMP PDE5 with 2.0- and 12.9-fold selectivity over PDE3 and PDE4, respectively[1]. Kuraridine induces pronounced chloride inward currents in the absence of GABA. Thecurrents does not exceed 10% of the maximal IGABA induced by a saturating GABA concentration (1 mM)[2]. Kuraridine induces a concentration–response curves for IGABA enhancement (EC50=4.0±2.4 μM) in Xenopus oocytes expressing GABAA receptors composed of α1, β2, and γ2S subunits[2]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C26H30O6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 438.51300 |
| Exact Mass | 438.20400 |
| PSA | 107.22000 |
| LogP | 5.50480 |