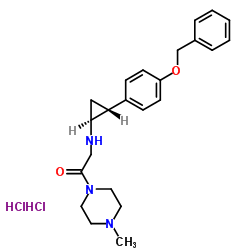
1781835-13-9
| Name | RN-1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ethanone, 1-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-[[(1S,2R)-2-[4-(phenylmethoxy)phenyl]cyclopropyl]amino]-, hydrochloride (1:2)
2-({(1S,2R)-2-[4-(Benzyloxy)phenyl]cyclopropyl}amino)-1-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)ethanone dihydrochloride |
| Description | RN-1 dihydrochloride is a potent, brain-penetrant, irreversible and selective lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) inhibitor with an IC50 of 70 nM. RN-1 dihydrochloride exhibits selectivity for LSD1 over MAO-A and MAO-B with IC50 values of 0.51 μM and 2.785 μM respectively[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 70 nM (LSD1), 0.51 μM (MAO-A) and 2.785 μM (MAO-B)[1] |
| In Vitro | RN-1 dihydrochloride shows cytotoxic for ovarian cancer cells (SKOV3, OVCAR3, A2780 and cisplatin-resistant A2780cis), with IC50 values of ≈100-200 μM[3]. |
| In Vivo | RN-1 (3-10 mg/kg; i.p.; daily; for 2 or 4 consecutive weeks) dihydrochloride effectively induces fetal hemoglobin (HbF) levels in red blood cells and reduces disease pathology in SCD mice[2]. In C57BL/6 male mice, after intraperitoneal administration of RN-1 dihydrochloride (10 mg/kg), concentrations are detectable up to 24 h post dose in both plasma and brain tissues. The brain/plasma exposure ratio is 88.9. RN-1 dihydrochloride significantly impairs long-term memory, but not short-term memory[1]. Animal Model: Sickle cell disease (SCD) mice[2] Dosage: 3 mg/kg or 10 mg/kg Administration: i.p.; daily; for 2 or 4 consecutive weeks Result: Effectively induced HbF levels in red blood cells and reduced disease pathology in SCD mice. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C23H31Cl2N3O2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 452.42 |
| Exact Mass | 451.179321 |