953778-63-7
| Name | TTA-A2 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
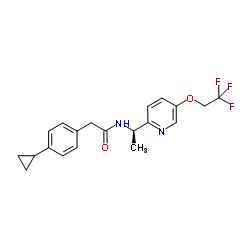
2-(4-Cyclopropylphenyl)-N-{(1R)-1-[5-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-2-pyridinyl]ethyl}acetamide
TTA-A2 |
| Description | TTA-A2 is a potent, selective and orally active t-type voltage gated calcium channel antagonist with reduced pregnane X receptor (PXR) activation. TTA-A2 is equally potent against the Cav3.1 (a1G) and Cav3.2 (a1H) channels with IC50 values of 89 nM and 92 nM, respectively, at -80 and -100 mV holding potentials. TTA-A2 can be used for the research of a variety of human neurological diseases, including sleep disorders and epilepsy[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 98 nM ( α1I at membrane holding potentials of -80 mV) IC50: 3.7 μM (α1I at membrane holding potentials of -100 mV)[1] |
| In Vitro | TTA-A2 exhibits a state-dependent inhibition of α1I with potencies of 98 nM and 3.7 μM at membrane holding potentials of -80 and -100 mV, respectively in astandard voltage-clamp electrophysiology assay. It also exhibits excellent selectivity against the Cav1.2 (L-type), Cav2.1 (P/Q-type), Cav2.2 (N-type), and Cav2.3 (R-type) channels which all had IC50 values of >30 μM at 80 mV[1]. TTA-A2 exhibits high affinity in the α1I binding assay with a Ki of 1.2 nM and has excellent selectivity over the hERG potassium channel and L-type calcium channel (both IC50>10 μM)[1]. |
| In Vivo | TTA-A2 (oral gavage; 3 mg/kg; single dose) produces significant changes in sleep architecture in rats. A reduction in active wake soon after dosing with a concurrent increase in delta sleep and decrease in REM sleep. Additionally, these effects persists for up to 4 h post-dose in rats[1]. TTA-A2 (oral gavage; 10 mg/kg; once daily; 5 days) shows selective effect on recurrent thalamocortical network activity, it suppresses active wake and promotes slow-wave sleep in wild-type mice but not in mice lacking both Cav3.1 and Cav3.3[2]. Animal Model: Wild-type and double Cav3.1/Cav3.3 knockout C57BL6/Sv129 background mices[2] Dosage: 10 mg/kg Administration: Oral gavage; 10 mg/kg; once daily; 5 days Result: Blocked active wake and promotes slow-wave sleep in wild-type mice but not mutant mice. |
| References |
[1]. Thomas S Reger, et al.Pyridyl amides as potent inhibitors of T-type |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 538.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C20H21F3N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 378.388 |
| Flash Point | 279.5±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 378.155518 |
| LogP | 3.58 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.545 |