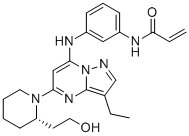
2020052-55-3
| Name | CDK12 inhibitor E9 S-isomer |
|---|
| Description | CDK12 inhibitor E9 S-isomer (E9, CDK12-IN-E9) is a clinical analog of THZ1 and a selective, covalent CDK12 inhibitor that is not susceptible to ABC transporter-mediated drug efflux; dose-dependently decreases phosphorylated and total RNAPII in THZ1R NB and lung cancer models, competed strongly with bio-THZ1 for binding to CDK12 at low nanomolar ranges, but not CDK7 (>1 uM); exerts its cytotoxic effects through covalent modification of cysteine 1039 of CDK12; shows more potent antiproliferative activity in THZ1R NB and lung cancer cells with IC50 ranging from 8 to 40 nM than ribociclib, palbociclib, and AZD5438. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
CDK12 CDK9/cyclinT1:23.9 nM (IC50) cdk2/cyclin A:932 nM (IC50) CDK7/Cyclin H/MNAT1:1210 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | CDK12-IN-E9 (E9; 10 nM-10 μM; 72 hours; Kelly, LAN5, SK-N-BE2, PC-9, NCI-H82 and NCI-H3122 cells) treatment shows potent antiproliferative activity in THZ1R NB and lung cancer cells, with IC50 values ranging from 8 to 40 nM[1]. CDK12-IN-E9 (E9; 0-3000 nM; 6 hours; Kelly, PC-9, and NCI-H82 cells) treatment leads to a dose-dependent decrease in phosphorylated and total RNAPII in THZ1r NB and lung cancer models, accompanied by decreased MYC and MCL1 expression[1]. CDK12-IN-E9 also results in increased PARP cleavage, and an increase in the subGI population in THZ1r lung cancer cells, while in NB cells, more of a G2/M arrest is seen after a 24-hr exposure to CDK12-IN-E9[1]. Cell Proliferation Assay[1] Cell Line: Kelly, LAN5, SK-N-BE2, PC-9, NCI-H82 and NCI-H3122 cells Concentration: 10 nM-10 μM Incubation Time: 72 hours Result: Showed potent antiproliferative activity in THZ1R NB and lung cancer cells, with IC50 values ranging from 8 to 40 nM. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: Kelly, PC-9, and NCI-H82 cells Concentration: 0 nM, 30 nM, 100 nM, 300 nM, 1000 nM, 3000 nM Incubation Time: 6 hours Result: Led to a dose-dependent decrease in phosphorylated and total RNAPII in THZ1r NB and lung cancer models. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C24H30N6O2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 434.544 |