52455-32-0
| Name | Ethyl 3-ethyl-2-methyl-4-oxo-2-cyclohexene-1-carboxylate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
2-Cyclohexene-1-carboxylic acid, 3-ethyl-2-methyl-4-oxo-, ethyl ester
MFCD00001579 Ethyl 3-ethyl-2-methyl-4-oxo-2-cyclohexene-1-carboxylate Ethyl 3-ethyl-2-methyl-4-oxocyclohex-2-ene-1-carboxylate |
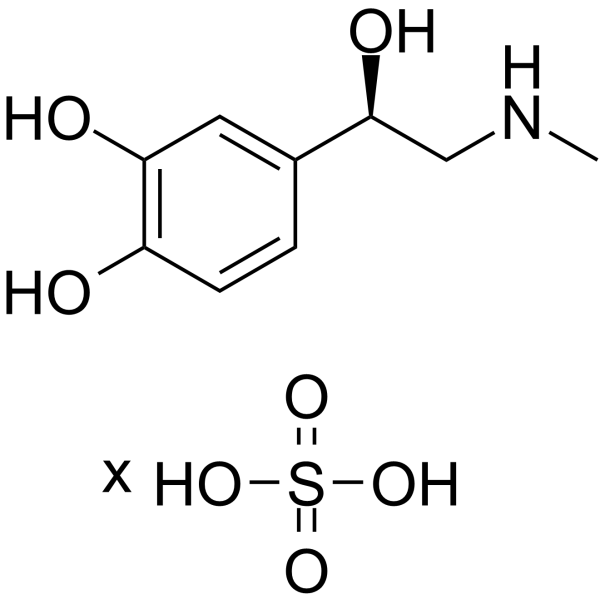
| Description | Adrenaline sulfate is a orally active hormone secreted by the medulla of the adrenal glands. Adrenaline sulfate is an α-adrenergic and β-adrenergic receptor agonist. Adrenaline sulfate can be used in the treatment of anaphylaxis. Adrenaline sulfate has the potential for the research of cardiac arrest[1][2][3][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vivo | Adrenaline sulfate (0.75, 1.5, 3 mg/kg; i.p.) exerts oxidative and nitrative stress in rats, increased damage to lipids and proteins, and damage of cardiomyocytes and cytogenetic damage in rats[2]. Adrenaline sulfate (0.02, 0.03 mg/kg) increases ABP’s and to some extent also CePP, but significantly decreases organ and brain perfusion in adult pigs[3]. Adrenaline sulfate (0.1 mg/kg; s.c.) enhances memory in young adult rats, in part, by increasing blood glucose levels needed to modulate memory[6]. Animal Model: 220-280 g, 18 weeks Wistar rats[2] Dosage: 0.75, 1.5, 3 mg/kg Administration: IP Result: Induced a significant rise in CAT activity, MDA level, PCC, NO2−, and 3-NT and a significant decrease in SOD activity, and exerted an increase in total activity of LDH, LDH1, and LDH2 isoenzymes. Animal Model: 24-25 month male Fischer-344 rats[6] Dosage: 0.1 mg/kg Administration: S.c. Result: Enhanced memory in young adult rats, in part, by increasing blood glucose levels needed to modulate memory. |
| References |
[4]. Callaway CW. Epinephrine for cardiac arrest. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2013 Jan;28(1):36-42. |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 301.3±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C12H18O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 210.270 |
| Flash Point | 129.0±27.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 210.125595 |
| LogP | 2.29 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.471 |