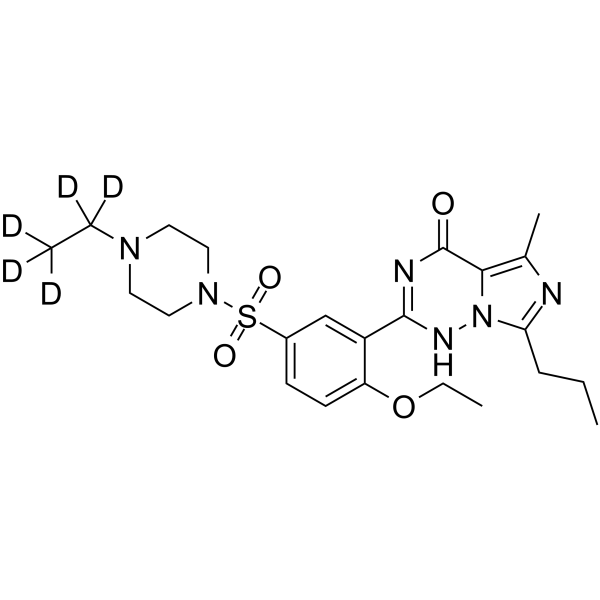
1189685-70-8
| Name | 2-[2-ethoxy-5-[4-(1,1,2,2,2-pentadeuterioethyl)piperazin-1-yl]sulfonylphenyl]-5-methyl-7-propyl-1H-imidazo[5,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-4-one |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Vardenafil-d5
Nuviva-d5 Levitra-d5 2-(2-Ethoxy-5-{[4-(H)ethyl-1-piperazinyl]sulfonyl}phenyl)-5-methyl-7-propylimidazo[5,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-4(1H)-one |
| Description | Vardenafil-d5 is deuterium labeled Vardenafil. Vardenafil is a selective, orally active, potent inhibitor of phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5), with an IC50 of 0.7 nM. Vardenafil shows selectivity over PDE1 (180 nM), PDE6 (11 nM), PDE2, PDE3, and PDE4 (>1000 nM). Vardenafil competitively inhibits cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) hydrolysis and thus increases cGMP levels. Vardenafil can be used for the research of erectile dysfunction[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 692.3±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C23H27D5N6O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 493.63 |
| Flash Point | 372.5±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 493.251953 |
| PSA | 121.28000 |
| LogP | 2.65 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.656 |