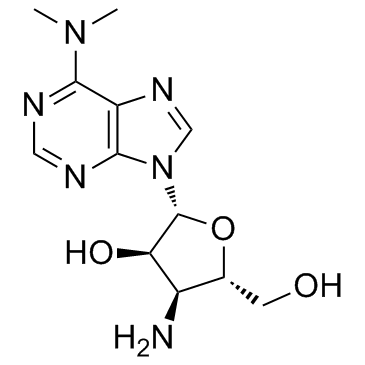
53-79-2
| Name | puromycin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
PUROMYCIN
p-638 Stylomycin L-3'-(a-Amino-p-methoxyhydrocinnamamido)-3'-deoxy-N,N-dimethyladenosine 3123l (S)-3'-[[2-Amino-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-oxopropyl]amino]-3'-deoxy-N,N-dimethyladenosine puromycinum [INN_la] 1-mm 6-Dimethylamino-9-[3-deoxy-3-(p-methoxy-L-phenylalanylamino)-b-D-ribofuranosyl]-b-purine cl13,900 3'-{(E)-[(2S)-2-Amino-1-hydroxy-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)propylidene]amino}-3'-deoxy-N,N-dimethyladenosine 3123-L 3'-(a-Amino-p-methoxyhydrocinnamamido)-3'-deoxy-N,N-dimethyladenosine Stillomycin achromycin 3'-Deoxy-N,N-dimethyl-3'-[(O-methyl-L-tyrosyl)amino]adenosine |
| Description | Puromycin dihydrochloride is the dihydrochloride salt of puromycin. Puromycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that inhibits protein synthesis. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Puromycin blocks protein synthesis after aminoacyl-sRNA formation, and at the same time it leads to the accumulation of small peptides. Both of these effects appear to be due to the splitting of ribosome-bound peptidyl-sRNA,4 which results in release of incomplete peptide chains.[1]. Puromycin, an analog of the 3' end of aminoacyl-tRNA, causes premature termination of translation by being linked non-specifically to growing polypeptide chains. Puromycin has two modes of inhibitory action. The first is by acting as an acceptor substrate which attacks peptidyl-tRNA in the P site to form a nascent peptide. The second is by competing with aminoacyl-tRNA for binding to the A' site[2]. When used in minimal amounts, puromycin incorporation in neosynthesized proteins reflects directly the rate of mRNA translation in vitro. Puromycin immunodetection is an advantageous alternative to radioactive amino acid labeling. It allows the direct evaluation of translation activity in single cells by immunofluorescence microscopy and in heterogenous populations of cells by fluorescenceactivated cell sorting[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 175.5-177ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C22H29N7O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 471.510 |
| Exact Mass | 471.223022 |
| PSA | 160.88000 |
| LogP | 0.93 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.701 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| RIDADR | UN 3249 |
|---|---|
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(b) |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |

![3'-[(N-benzyloxycarbonyl-O-methyl-tyrosyl)-amino]-N6,N6-dimethyl-3'-deoxy-adenosine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/175/57182-86-2.png)
![3'-[(N-tert-butoxycarbonyl-O-methyl-tyrosyl)-amino]-N6,N6-dimethyl-3'-deoxy-adenosine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/043/57183-05-8.png)

![9-[3-(benzylamino)-3-N,2-O-carbonyl-3-deoxy-β-D-ribofuranosyl]adenine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/315/125084-71-1.png)