19186-33-5
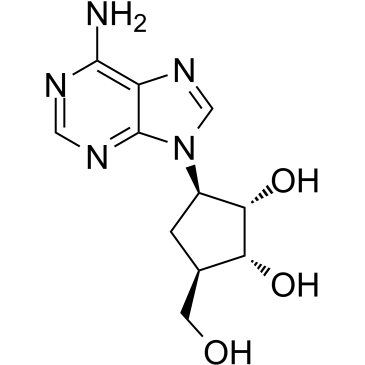
| Name | Aristeromycin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Cycloadenosine
carbocyclic adenosine 4'-O-Carbaadenosine |
| Description | Aristeromycin, an adenosine analog, is an antibiotic and a potent S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (AHCY) inhibitor[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase[1] |
| In Vitro | The IC50 value of Aristeromycin against AHCY is 38.5 nM at 50 μM SAH (approximately equal to the Km: 48 μM), but 271 nM at 1000 µM SAH (20× Km). With 60 min of preincubation, the mean IC50 value of Aristeromycin at 50 μM SAH is 12.7 nM[1]. Aristeromycin has IC50 values of 3.2 μM for LNCaP-FGC cell growth and 0.88 μM for LNCaP-hr cell growth[1]. At least in part, Aristeromycin can regulate oncogenic EZH2 expression by inducing miR-26a[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.92g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 595.1ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C11H15N5O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 265.26900 |
| Flash Point | 313.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 265.11700 |
| PSA | 130.31000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 5.19E-15mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.881 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|---|---|
| RTECS | GY4250000 |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
![(1R,2S,3R,4R)-4-(acetoxymethyl)-2,3-[(dimethylmethylene)dioxy]-cyclopentane-1-carboxamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/331/84955-45-3.png)

![(1R,2S,3R,4R)-4-(acetoxymethyl)-1-[(tert-butoxycarbonyl)amino]-2,3-[(dimethylmethylene)dioxy]-cyclopentane structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/293/84955-46-4.png)
![(4R,5R)-1-(2,2-dimethyl-5-vinyl-[1,3]dioxolan-4-yl)prop-2-en-1-ol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/060/683276-43-9.png)
![6H-Purin-6-one,9-[(1R,2S,3R,4R)-2,3-dihydroxy-4-(hydroxymethyl)cyclopentyl]-1,9-dihydro structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/296/16975-94-3.png)