24047-25-4
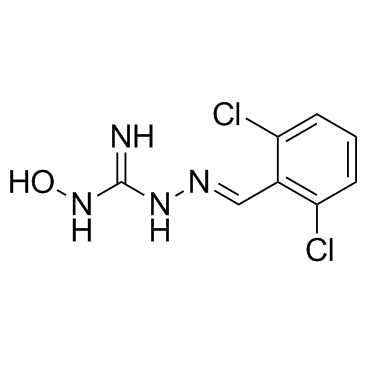
| Name | 2-[(E)-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)methylideneamino]-1-hydroxyguanidine |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
UNII-P9HIK5V7WK
Guanoxabenz Hydrazinecarboximidamide,2-((2,6-dichlorophenyl)methylene)-N-hydroxy Guanoxabenz (USAN/INN) 1-(2,6-dichlorobenzylideneamino)-3-hydroxyguanidine |
| Description | Guanoxabenz is an α2 adrenergic receptor agonist. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Adrenergic receptor[1] |
| In Vitro | The formation of high-affinity Guanoxabenz binding seems to be inhibited by a series of N-hydroxyguanidine analogs to Guanoxabenz, as well as by a series of metabolic inhibitors that included allopurinol, 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene, 5,59-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid), cibacron blue, phenyl-p-benzoquinone, didox, and trimidox. The formation of Guanoxabenz high-affinity binding is also inhibited in a time- and concentration-dependent fashion by preincubating the membranes with the LW03 N-hydroxyguanidine analogue of Guanoxabenz[1]. The spleen cytosolic fraction mediates the reduction of Guanoxabenz to guanabenz, the latter having an almost 100-fold higher affinity for rat alpha2A-adrenoceptors than Guanoxabenz itself[2]. |
| In Vivo | Guanoxabenz and guanabenz are both known as centrally active antihypertensive drugs. enzymatic activity in the rat spleen can induce N-reduction of Guanoxabenz, leading to high affinity alphaα2 adrenergic receptor binding, due to the formation of theα2 adrenergic receptor active drug, guanabenz. High affinity Guanoxabenz binding is also induced in rat brain membranes after addition of NADH or NADPH cofactors. The rat cerebral cortex contains an enzymatic activity that may activate Guanoxabenz leading to formation of a metabolite showing high affinity for alpha 2-adrenoceptors[3]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 435.6ºC at 760mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C8H8Cl2N4O |
| Molecular Weight | 247.08100 |
| Flash Point | 217.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 246.00800 |
| PSA | 80.50000 |
| LogP | 2.71200 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |