956029-28-0
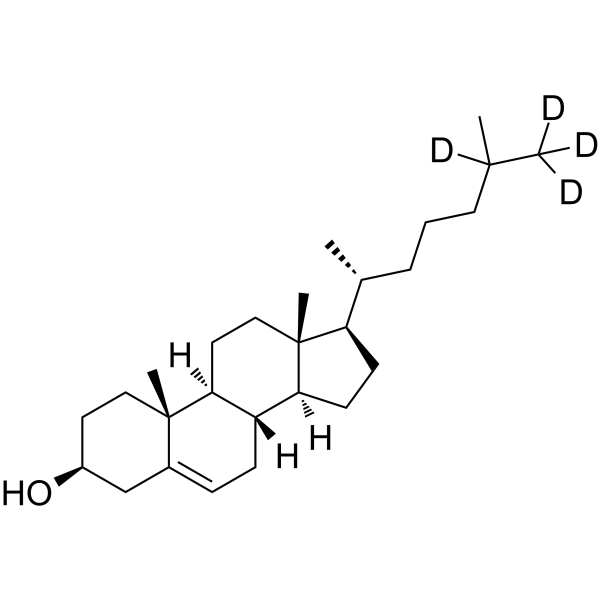
| Name | (3S,8S,9S,10R,13R,14S,17R)-10,13-dimethyl-17-[(2R)-6,7,7,7-tetradeuterio-6-methylheptan-2-yl]-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-ol |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
5:6-Cholesten-3|A-ol-d4
Cholesterin-d4 Cholesterol-d4 Cholest-5-en-3|A-ol-d4 5-Cholesten-3|A-ol-d4 Lidinite-d4 Dythol-d4 Provitamin D-d4 Lidinit-d4 |
| Description | Cholesterol-d4 is deuterium labeled Cholesterol. Cholesterol is the major sterol in mammals and is makes up 20-25% of structural component of the plasma membrane. Plasma membranes are highly permeable to water but relatively impermeable to ions and protons. Cholesterol plays an important role in determining the fluidity and permeability characteristics of the membrane as well as the function of both the transporters and signaling proteins[1][2]. Cholesterol is also an endogenous estrogen-related receptor α (ERRα) agonist[3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C27H42D4O |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 390.68 |
| Exact Mass | 390.38000 |
| PSA | 20.23000 |
| LogP | 7.38870 |