75530-68-6
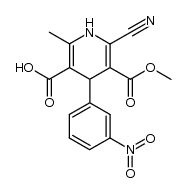
| Name | 3-O-methyl 5-O-propan-2-yl 2-cyano-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
3,5-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 2-cyano-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-, 3-methyl 5-(1-methylethyl) ester
Nivadipine 4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate Nilvadipine Nilvadipine [USAN:INN:JAN] Nilvadipino [Spanish] 5-Isopropyl 3-methyl 2-cyano-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydro-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate UNII:0214FUT37J Isopropyl 6-Cyano-5-methoxycarbonyl-2-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxylate 3-methyl 5-propan-2-yl 2-cyano-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate 5-Isopropyl 3-methyl 2-cyano-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate Nivaldipine isopropyl 6-cyano-5-methoxycarbonyl-2-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-1 Escor 5-isopropyl-3-methyl-2-cyano-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate Nivadil Nilvadipinum [Latin] 2-Cyano-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylic Acid 3-Methyl 5-(1-Methylethyl) Ester 5-Isopropyl-3-methyl-2-cyano-1,4-dihydro-6-methyl-4-(m-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate |
| Description | Nilvadipine is a potent calcium channel antagonist, and the IC50 value is around 0.1 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 0.1 nM (Calcium channel)[1] |
| In Vitro | In an in vitro experiment on inhibition of migration of rat aortic smooth muscle cells, using Zymosan-activated air pouch exudate as a chemoattractant in modified Boyden chambers.The IC50 value is 0.033 nM for Nilvadipine (FR34235). Effects of Nilvadipine on proliferation of rat aortic smooth muscle cells and rabbit platelet aggregation is also examined. Nilvadipine should be useful for preventing and treating atherosclerosis. Inhibition of smooth muscle cell migration is thought to be its mechanism of antiatherogenic activity[2]. The antioxidant effect of calcium antagonist Nilvadipine is studied by means of rat myocardial membrane lipid peroxidation with a nonenzymatic active oxygen-generating system (DHF/FeC13-ADP) with IC50 of 25.1 μM. Nilvadipine shows antioxidant effects both before and after the addition of active oxygen, and reduces the dihydroxyfumarate (DHF) auto-oxidation rate, is chain-breaking and preventive antioxidants. Nicardipine, which shows an antioxidant effect only before exposure to active oxygen and reduced the DHF auto-oxidation rate, is mainly a preventive antioxidant[3]. |
| In Vivo | The antiatherogenic activity of Nilvadipine (FR34235), a calcium antagonist, is examined in rabbits with carotid arteries sheathed with polyethylene cuffs, and compared with that of Nifedipine, Verapamil and Diltiazem. Nilvadipine is given intramuscularly in daily doses of 0.01-10 mg/kg for 3 weeks, starting on the day of cuff-placement. FR34235 dose-dependently inhibits the cuff-induced intimal thickening[2]. Nilvadipine affords significant protection against thinning of retinal layers in the RCS rat during retinal degeneration. Electron microscopy shows that marked irregularity in the photoreceptor OS in the untreated retina[4]. |
| Animal Admin | Rat[4] In the present study, 3- to 5-week-old inbred RCS (rdy-/-) rats reared in cyclic light conditions (12 hours on-12 hours off) are used. Nilvadipine and Nifedipine are dissolved in a mixture of ethanol, polyethylene glycol 400, and distilled water (2:1:7) at a concentration of 0.1 mg/mL, diluted twice with physiological saline before use, and injected intraperitoneally (1.0 mL/kg) into anesthetized rats every day early in the morning for 2 weeks. In control rats, the same solution without Nilvadipine or Nifedipine (vehicle solution) is administered similarly. Nicardipine and Diltiazem are dissolved in PBS at 0.25 mg/mL and 1 mg/mL, respectively, and injected intraperitoneally (1 mL/kg), similarly to the other agonists. As a control, the same volume of a mixture of ethanol, polyethylene glycol 400, and distilled water (2:1:7) or PBS is administered. Before administration, the pH of all drug solutions is adjusted to approximately 7.4. The concentrations of these drugs administered to RCS rats are determined by their concentrations in oral administration to human patients with hypertension for 1 day in our clinical practice (Nilvadipine, 0.05-0.3 mg/kg; Nifedipine, 0.1-0.5 mg/kg; Nicardipine, 0.2-1 mg/kg; and Diltiazem, 0.3-3 mg/kg). |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 526.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 148-150ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C19H19N3O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 385.371 |
| Flash Point | 272.3±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 385.127380 |
| PSA | 134.24000 |
| LogP | 1.72 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.584 |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: soluble15mg/mL, clear |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 22 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | US7968300 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
![3,5-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2-[(hydroxyimino)methyl]-6-methyl-4-(3-nitrophenyl)-, 3-methyl 5-(1-methylethyl) ester structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/073/1452166-70-9.png)