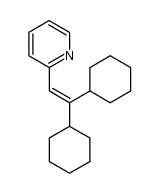
6621-47-2
| Name | perhexiline |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | perhexilene |
| Description | Perhexiline is an orally active CPT1 and CPT2 inhibitor that reduces fatty acid metabolism. Perhexiline induces mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in hepatic cells. Perhexiline can cross the blood brain barrier (BBB) and shows anti-tumor activity. Perhexiline can be used in the research of cancers, and cardiovascular disease like angina[1][2][5]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Perhexiline (5-25 μM, 2-6 h) reduces cell viability in HepG2 cells[2]. Perhexiline (5-25 μM, 2-6 h) reduces cellular ATP content and Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release in HepG2 cells[2]. Perhexiline (20 μM, 2 h) activates caspase 3/7 in HepG2 cells[2]. Perhexiline (5-25 μM, 4 h) causes mitochondrial dysfunction in HepG2 cells[2]. Perhexiline (5 μM, 48 h) selectively induces massive apoptosis in CLL cells (high expression of CPT)[3]. Cell Viability Assay[2] Cell Line: HepG2 cells Concentration: 5, 10, 15, 25 μM Incubation Time: 2, 4, 6 h Result: Induced time- and concentration-dependent cytotoxicity in hepatic cells. Western Blot Analysis[2] Cell Line: HepG2 cells Concentration: 5, 10, 15, 25 μM Incubation Time: 2 h Result: Reduced Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 level, and increased Bad level. |
| In Vivo | Perhexiline (200 mg/kg, p.o., daily for 8 weeks) reduces peripheral neural function in female DA rats[4]. Perhexiline (80 mg/kg, oral gavage, for 3 days) demonstrates anti-tumor activity in glioblastoma mouse model[5]. Animal Model: Orthotopic glioblastoma mouse model[5] Dosage: 80 mg/kg Administration: Oral gavage, for 3 days. Result: Reduces tumor size (MR imaging) and improves in overall survival. |
| Boiling Point | 340ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C19H35N |
| Molecular Weight | 277.48800 |
| Flash Point | 164.5ºC |
| Exact Mass | 277.27700 |
| PSA | 12.03000 |
| LogP | 5.62420 |
|
~% 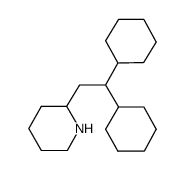
6621-47-2 |
| Literature: Richardson-Merrell Inc. Patent: US4069222 A1, 1978 ; |
|
~% 
6621-47-2 |
| Literature: Schou, Soren Christian Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals, 2010 , vol. 53, # 1 p. 31 - 35 |