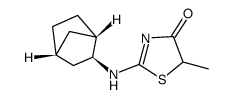
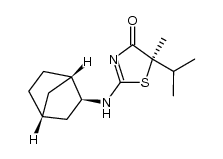
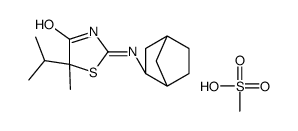
1095565-81-3
| Name | (5S)-2-[[(1R,3S,4S)-3-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptanyl]amino]-5-methyl-5-propan-2-yl-1,3-thiazol-4-one |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
5S-2-(bicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-ylamino)-5-isopropyl-5-methylthiazol-4(5H)-one
UNII-2T929W7AG8 4(5H)-Thiazolone,2-((1S,2S,4R)-bicyclo(2.2.1)hept-2-ylamino)-5-methyl-5-(1-methylethyl)-,(5S) AMG 221 (S)-2-((1S,2S,4R)-bicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-ylamino)-5-isopropyl-5-methylthiazol-4(5H)-one |
| Description | AMG-221 is an inhibitor of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11β-HSD1) with a Ki of 12.8 nM in vitro biochemical scintillation proximity assay (SPA) and an IC50 of 10.1 nM in cell-based assays[1][2]. AMG-221 can be used for the research of type 2 diabetes[3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | AMG-221 shows selectivity over 11β-HSD2, 17β-HSD1, and glucocorticoid receptor (GR) (IC50 values for all assays are >10 μM)[2]. |
| In Vivo | AMG-221 (25 or 50 mg/kg; b.i.d.; orally gavaged) inhibits 11β-HSD1 activity in DIO mice. At the end of the study, fed blood glucose shows statistically significant reduction in comparison to the vehicle group. On day 14 and after a 12 h fast, glucose tolerance is slightly improved in the AMG-221 treatment groups compared with the vehicle group[2]. 11β-HSD1 activity is inhibited by 33%, 55%, and 47% in the inguinal fat at 4 h after AMG-221 is orally gavaged at 5, 15, and 50 mg/kg, respectively. At 8 h, the 11β-HSD1 activity in the inguinal fat of the 5 mg/kg group has returned to a level (∼10% inhibition) close to that in the control animals treated with vehicle, but there is still significant inhibition in the 15 and 50 mg/kg groups (36% and 39% inhibition, respectively)[2]. AMG-221 has a good bioavailability in mouse, rat, and dog. However, the bioavailability in monkey is low[2]. AMG-221 exhibits moderate oral bioavailability (male CD1 mouse 31%) following oral administration (10 mg/kg)[3]. AMG-221 exhibits terminal elimination half-life (male CD1 mouse 3.32 h) due to high plasma clearance (3.31 L/h/kg) combined with large volumes of distribution (0.9 L/kg) following intravenous administration (2 mg/kg)[3]. Animal Model: Diet-Induced Obesity (DIO) Mice[2] Dosage: 25 or 50 mg/kg (prepare in 0.1% Tween-80 and 0.5% CMC in water) Administration: Orally gavaged; twice a day for 13 or 14 days Result: There were statistically significant decreases in insulin levels in all treated groups when compared with the vehicle control group on day 13. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C14H22N2OS |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 266.40200 |
| Exact Mass | 266.14500 |
| PSA | 70.25000 |
| LogP | 3.08460 |
|
~68% 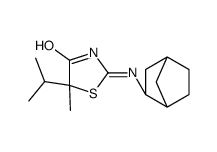
1095565-81-3 |
| Literature: AMGEN INC. Patent: WO2009/2445 A1, 2008 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 44-45 ; WO 2009/002445 A1 |
|
~% 
1095565-81-3 |
| Literature: AMGEN INC.; CAILLE, Seb; CUI, Sheng; WANG, Silas; FAUL, Margaret Patent: WO2010/14586 A1, 2010 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 24-25 ; WO 2010/014586 A1 |
|
~% 
1095565-81-3 |
| Literature: Frizzle, Matthew J.; Nani, Roger R.; Martinelli, Michael J.; Moniz, George A. Tetrahedron Letters, 2011 , vol. 52, # 43 p. 5613 - 5616 |
|
~92% 
1095565-81-3 |
| Literature: AMGEN INC.; MONIZ, George A.; FRIZZLE, Matthew J.; BERNARD, Charles; MARTINELLI, Michael; FAUL, Margaret; LARROW, Jay; HANSEN, Karl B.; KLINGENSMITH, Liane Patent: WO2010/8729 A2, 2010 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 45-46 ; WO 2010/008729 A2 |
| Precursor 4 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |