5284-44-6
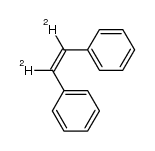
| Name | TRANS-STILBENE-α,α'-D2 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
1-Propene,1,2-dichloro
trans-<1,2-2H2>stilbene trans-1,3-dichloropropylene 1c,2-dichloro-propene Propene,1,2-dichloro trans-1,2-Dichloropropene 1c,2-Dichlor-propen trans-1,2-dideuteriostilbene |
| Description | trans-Stilbene-d2 is the deuterium labeled trans-Stilbene[1]. trans-Stilbene ((E)-Stilbene) is used in the manufacturing of dye lasers, optical brighteners, non-steroidal synthetic estrogens[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C14H10D2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 182.25700 |
| Exact Mass | 182.10600 |
| LogP | 3.85700 |
|
~96% 
5284-44-6 |
| Literature: Shirakawa, Eiji; Otsuka, Hidehito; Hayashi, Tamio Chemical Communications, 2005 , # 47 p. 5885 - 5886 |
|
~% 
5284-44-6 |
| Literature: Tani, Kazuhide; Iseki, Aika; Yamagata, Tsuneaki Chemical Communications, 1999 , # 18 p. 1821 - 1822 |
|
~85% 
5284-44-6 |
| Literature: Tse, Sunny Kai San; Xue, Peng; Lin, Zhenyang; Jia, Guochen Advanced Synthesis and Catalysis, 2010 , vol. 352, # 9 p. 1512 - 1522 |
|
~75% 
5284-44-6 |
| Literature: Tse, Sunny Kai San; Xue, Peng; Lin, Zhenyang; Jia, Guochen Advanced Synthesis and Catalysis, 2010 , vol. 352, # 9 p. 1512 - 1522 |
|
~% 
5284-44-6 |
| Literature: Saltiel, Jack; Waller, Andrew S.; Sears, Donald F.; Garrett, Christopher Z. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1993 , vol. 97, # 11 p. 2516 - 2522 |
|
~0% 
5284-44-6 |
| Literature: Belger, Christian; Neisius, N. Matthias; Plietker, Bernd Chemistry - A European Journal, 2010 , vol. 16, # 40 p. 12214 - 12220 |