124750-99-8
| Name | Losartan potassium |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
MK 954
potassium salt {2-Butyl-5-chloro-3-[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)-biphenyl-4-ylmethyl]-3H-imidazol-4-yl}-methanol {2-BUTYL-5-CHLORO-3-[2'-(1H-TETRAZOL-5-YL)-BIPHENYL-4-YLMETHYL]-3H-IMIDAZOL-4-YL}-METHANOL POTASSIUM SALT 5-(4'-{[2-butyl-4-chloro-5-(hydroxyméthyl)-1H-imidazol-1-yl]méthyl}biphényl-2-yl)tétrazol-1-ide de potassium Lortaan Losartan potassium 2-BUTYL-4-CHLORO-1-[[2'-(1H-TETRAZOL-5-YL)[1,1'-BIPHENYL]-4-YL]METHYL]-1H-IMIDAZOLE-5-METHANOL MONOPOTASSIUM SALT Losaprex COZAAR Losartan potassium salt EINECS 200-287-4 Losartanpatassium mk-0954 Du Pont 753 Losartan (potassium salt) 1H-imidazole-5-methanol, 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-, monopotassium salt Losartan Potassium (DuP 753) Potassium 5-(4'-{[2-butyl-4-chloro-5-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-imidazol-1-yl]methyl}biphenyl-2-yl)tetrazol-1-ide LOSARTAN, POTASSIUM SALT Potassium 5-(4'-{[2-butyl-4-chloro-5-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-imidazol-1-yl]methyl}-2-biphenylyl)tetrazol-1-ide Aradois Potassium (2-butyl-4-chloro-1-{[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]methyl}-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methanolate thanolpotassium Potassium (2-butyl-4-chloro-1-{[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)-4-biphenylyl]methyl}-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methanolate LOSARTAN MONOPOTASSIUM SALT 1H-Imidazole-5-methanol, 2-butyl-4-chloro-1-[[2'-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl]methyl]-, potassium salt (1:1) LOSARTANPOTASSIUM Losartan (potassium) dupont753 MK-95 potassium (2-butyl-4-chloro-1-{[2'-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]methyl}-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methanolate LOSARTAN POTASSIUM, EP STAANDARD LOSARTAN POTASSIUM(SUBJECT TO PATENT FREE) DUP 753 MFCD02092704 |
| Description | Losartan (potassium) is an angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1) antagonist, competing with the binding of angiotensin II to AT1 with an IC50 of 20 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 20 nM (angiotensin II) |
| In Vitro | Losartan competes with the binding of angiotensin II to AT1 receptors. The concentration that inhibits 50% of the binding of angiotensin II (IC50) is 20 nM[1]. Losartan (40 μM) affects ISC but prevents the effect of ANGII on ISC[2]. Losartan significantly reduces Ang II-mediated cell proliferation in endometrial cancer cells. The combination of losartan and anti-miR-155 has a significantly greater antiproliferative effect compared to each drug alone[3]. |
| In Vivo | Losartan (0.6 g/L, p.o.) -treated Fbn1C1039G/+ mice show a reduction in distal airspace caliber relative to placebo-treated Fbn1C1039G/+ animals. The doses of losartan and propranolol are titrated to achieve comparable hemodynamic effects. Analysis of pSmad2 nuclear staining reveals that losartan antagonizes TGF-β signaling in the aortic wall of Fbn1C1039G/+ mice. Losartan can improve disease manifestations in the lungs, an event that cannot plausibly relate to improved hemodynamics[4]. Losartan (10 mg/kg, intraarterial injection) increases blood angiotensin levels four- to sixfold. Losartan (10 mg/kg, i.p.) increases plasma renin levels 100-fold; plasma angiotensinogen levels decreases to 24% of control; and plasma aldosterone levels are unchanged[5]. |
| Cell Assay | An MTT assay is used to measure cell proliferation and viability. For the assay, 5000 cells in 200 μL media per well are seeded in a 96 well plate. After overnight incubation to allow for cell attachment, the medium is removed by suction. MTT at 1 mg/mL concentration in serum-free medium is added and then incubated for 4 h at 37°C. After removal of MTT solution, 100 μL of DMSO is added to dissolve formazan crystals. Absorbance at 570 nm and at 600 nm as a reference is then measured using a microplate reader. The difference in absorbance is thus relative to the extent of cell survival. |
| Animal Admin | Female Fbn1C1039G/+ mice undergo timed matings with wild-type male mice. At 14.5d post-coitum, pregnant female Fbn1C1039G/+ mice are treated with oral losartan (0.6 g/L in drinking water; n=10), propranolol (0.5 g/L; n=6) or placebo (n=12). Therapy is continued throughout lactation and after weaning until 10 months of age. Mice are sacrificed and examined using the techniques described above. Propranolol is used for comparison with losartan because β-adrenergic receptor blockade is the current albeit controversial standard of care to modulate abnormal growth of the aortic root in MFS. Beginning at 7 weeks of age, wild-type and Fbn1C1039G/+ mice are treated with oral losartan (0.6 g/L in drinking water; n=5), propranolol (0.5 g/L; n=7) or placebo (n=10). Mice are continued on oral therapy for 6 months and then sacrificed. |
| References |
[1]. Burnier, M. Angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers. Circulation, 2001. 103(6): p. 904-12. |
| Density | 0.986 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 134 °C(lit.) |
| Melting Point | −69 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C22H22ClKN6O |
| Molecular Weight | 461.001 |
| Flash Point | 76 °F |
| Exact Mass | 460.118073 |
| PSA | 89.61000 |
| LogP | 3.89590 |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.55E-19mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | n20/D 1.387(lit.) |
| Storage condition | Desiccate at RT |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36/37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | NI6755100 |
| HS Code | 2933290090 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 4 | |
| HS Code | 2933290090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933290090. other compounds containing an unfused imidazole ring (whether or not hydrogenated) in the structure. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |



![[2-(1H-Tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl]boronic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/062/155884-01-8.png)
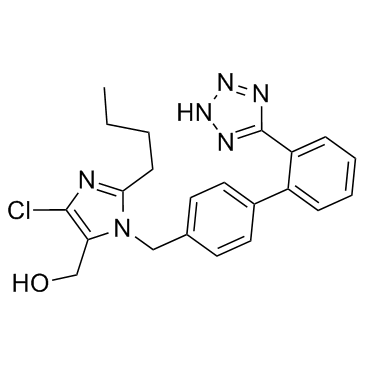
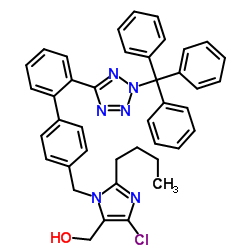
![2-BUTYL-4-CHLORO-5-(HYDROXYMETHYL)-1-{[2'-[(TRIPHENYLMETHYL)TETRAZOLE-5YL]BIPHENYL-4-YL]METHYL}IMIDAZOLE structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/244/124751-00-4.png)

![4'-[(2-Butyl-4-chloro-5-hydroxymethyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl]-1,1'-biphenyl-2-carbonitrile structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/021/114772-55-3.png)