92739-58-7
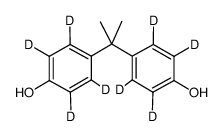
| Name | 2,3,5,6-tetradeuterio-4-[2-(2,3,5,6-tetradeuterio-4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-2-yl]phenol |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
2,2-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl-d4)propane
BisphenolA-(rings-d8) |
| Description | Bisphenol A-d8 is the deuterium labeled Bisphenol A[1]. Bisphenol A is a phenolic, organic synthetic compound widely used in the production of polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins. Bisphenol A is a reproductive, developmental, and systemic toxicant, often classified as an endocrine-disrupting compound (EDC). Bisphenol A is associated with many diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, respiratory diseases, diabetes, kidney diseases, obesity, and reproductivedisorders[2][3][4]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 220ºC4 mm Hg(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 157-159ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C15H8D8O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 236.33600 |
| Exact Mass | 236.16500 |
| PSA | 40.46000 |
| LogP | 3.42370 |
| Symbol |




GHS05, GHS07, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H317-H318-H335-H361f-H411 |
| Precautionary Statements | P280-P305 + P351 + P338 + P310 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |