64118-44-1
| Name | tridecanoic-2,2-d2 acid |
|---|
| Description | Tridecanoic acid-d2 is the deuterium labeled Tridecanoic acid. Tridecanoic acid (N-Tridecanoic acid), a 13-carbon medium-chain saturated fatty acid, can serve as an antipersister and antibiofilm agent that may be applied to research bacterial infections. Tridecanoic acid inhibits Escherichia coli persistence and biofilm formation[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 236ºC/100 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 41-42ºC(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C13H24D2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 216.36 |
| Flash Point | 113ºC |
| Exact Mass | 216.20600 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 4.38200 |
|
~% 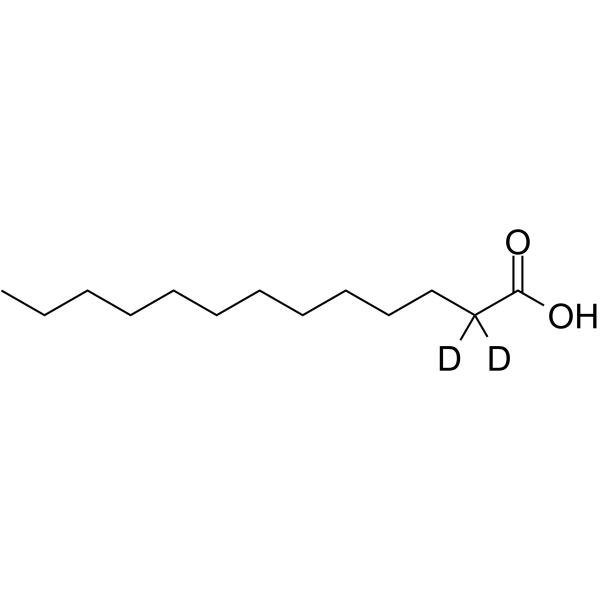
64118-44-1 |
| Literature: Poupko, R.; Luz, Z.; Spielberg, N.; Zimmermann, H. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1989 , vol. 111, # 16 p. 6094 - 6105 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |