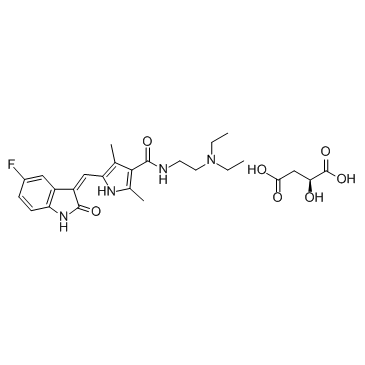
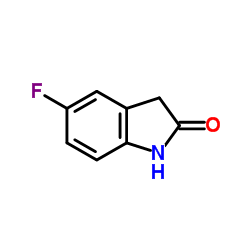
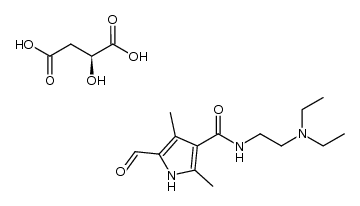
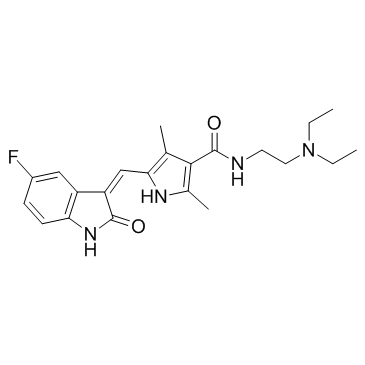
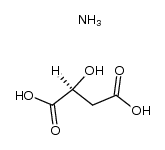
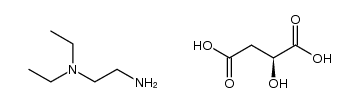
341031-54-7
| Name | Sunitinib Malate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
sunitinib L-malic acid salt
Sunitinib malate sunitynib L-malate L-malic acid salt of sunitinib Sunitinib (Malate) |
| Description | Sunitinib Malate (SU 11248 Malate) is a potent tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting VEGFR2 and PDGFRβ with IC50s of 80 nM and 2 nM, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
VEGFR2:80 nM (IC50) PDGFRβ:2 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Sunitinib Malate is also a good inhibitor of KIT and FLT-3[1]. In biochemical assays, Sunitinib (SU11248) exhibits competitive inhibition (with regard to ATP) against Flk-1 and PDGFRβ with Ki values of 9 nM and 8 nM, respectively. Sunitinib is also a competitive, albeit less potent, inhibitor of FGFR1 tyrosine kinase activity, with a Ki value of 0.83 μM. In addition to these three structurally related split kinase domain RTKs, the activity of Sunitinib has also been evaluated against a broad panel of additional tyrosine and serine/threonine kinases. In these biochemical assays, the IC50 values for Sunitinib are generally at least 10-fold higher than those for Flk-1 and PDGFR (e.g., IC50values of: >10 μM for EGFR and Cdk2; 4 μM for Met; 2.4 μM for IGFR-1; 0.8 μM for Abl; and 0.6 μM for Src)[2]. In RS4;11 cells (FLT3-WT), treatment with Sunitinib (SU11248) inhibits FLT3-WT phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner with IC50 of approximately 250 nM. In MV4;11 cells that express FLT3-ITD, Sunitinib inhibits FLT3-ITD phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner with an IC50 of 50 nM following a 2-hour treatment[3]. |
| In Vivo | Sunitinib Malate has very good oral bioavailability, is highly efficacious in a number of preclinical tumor models, and is well tolerated at efficacious doses[1]. Sunitinib (80 mg/kg/day) inhibits the growth of established SF763T and Colo205 tumor xenografts in athymic mice. Sunitinib (SU11248) treatment effectively inhibits the growth of established tumor xenografts[2]. Sunitinib malate is an inhibitor of VEGFR, PDGFR, FGFR, and is used in the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma and gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Sunitinib malate-treated rats display much lower levels of tumor growth than untreated rats, and their tumors have much smaller necrotic areas and lower vascular density[4]. |
| Kinase Assay | Biochemical assays to determine the activity of Sunitinib against different protein kinases are performed. Ki values for SU11248 against Flk-1, PDGFRβ, and FGFR1 are determined using glutathione S-transferase-fusion proteins containing the complete cytoplasmic domain of the RTK. Cellular assays to directly determine the ability of SU11248 to inhibit ligand-dependent RTK phosphorylation or cell proliferation and mitogenic responses are performed using serum-starved cells stimulated with 40 ng/mL VEGF165 (Flk-1/KDR), 0.5 μg/mL basic FGF (FGFR), or 50 ng/mL PDGF-AA (PDGFRα) or PDGF-BB (PDGFRβ)[2]. |
| Cell Assay | RS4;11 and MV4;11 cell lines are starved overnight in medium containing 0.1% FBS prior to addition of SU11248 (1 nM, 5 nM, 10 nM, 25 nM, 75 nM, 100 nM, 250 nM, 500 nM) and FL (50 ng/mL; FLT3-WT cells only). Proliferation is measured after 48 hours of culture using the Alamar Blue assay in triplicate for each condition, as described by the manufacturer. Trypan blue cell viability assays are performed in parallel and yielded similar results[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] Female nu/nu mice (8-12 weeks old, 25 g) are used. Briefly, 3-5×106 tumor cells are implanted s.c. into the hind flank region of mice on day 0. Daily treatment of tumor-bearing mice with oral administration of SU11248 as a carboxymethyl cellulose suspension or as a citrate buffered (pH 3.5) solution is initiated once the tumors reached the indicated average size. Tumor growth is evaluated based on twice-weekly measurement of tumor volume. Typically, studies are terminated when tumors in vehicle-treated animals reach an average size of 1000 mm3 or when the tumors are judged to adversely effect the well being of the animals. Rats[4] Forty female Sprague-Dawley rats (200-230 g) are used. Each group consists of 5-10 animals fed ad libitum. 1×104 Walker 256 cells are injected into the left abdominal mammary fat pad, under gas anesthesia (2% isoflurane). Rats are weighed daily and given Sunitinib malate (30 mg/kg) and/or Fingolimod (5 mg/kg) in olive oil by gavage. The tumors are measured with calipers. The animals are anesthetized and killed by an intracardiac injection of ketamine (50 mg/mL) before tumor ulceration. Rats are dissected to detect pulmonary, liver, kidney, or intestinal metastasis. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3600 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 156 °C(lit.) |
| Melting Point | 189-191°C |
| Molecular Formula | C26H33FN4O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 532.561 |
| Flash Point | 163 °F |
| Exact Mass | 532.233337 |
| PSA | 172.06000 |
| LogP | 2.77040 |
| Index of Refraction | n20/D 1.455(lit.) |
| Storage condition | Store at +4°C |
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H360-H372 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P308 + P313 |
| Hazard Codes | T |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |