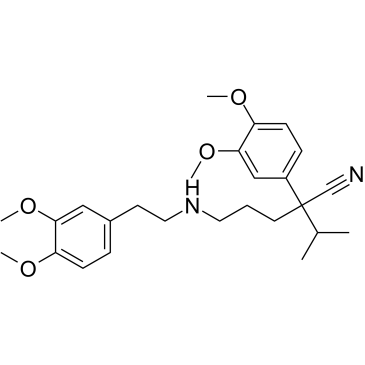
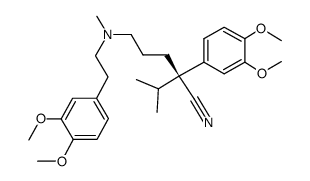
67018-85-3
| Name | norverapamil |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
N-desmethyl verapamil
Benzeneacetonitrile,a-[3-[[2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-ethyl]amino]propyl]-3,4-dimethoxy-a-(1-methylethyl) 5-[(3,4-dimethoxyphenethyl)amino]-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-isopropylvaleronitrile 2,8-bis(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-isopropyl-6-azaoctanenitrile 2-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-2-isopropyl-5-(3,4-dimethoxyphenethylamino)valeronitrile D591 (+/-)Nor-methylverapamil |
| Description | Norverapamil ((±)-Norverapamil), an N-demethylated metabolite of Verapamil, is a L-type calcium channel blocker and a P-glycoprotein (P-gp) function inhibitor[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Calcium channel blocker[1] P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitor[2] |
| In Vitro | Norverapamil ((±)-Norverapamil) is similarly effective as verapamil at inhibiting isoniazid and rifampicin tolerance and killing of intracellular M. tuberculosis in the absence of other drugs. norverapamil, also inhibits macrophage-induced tolerance and achieves similar serum levels to verapamil[1]. Verapamil and its major metabolite Norverapamil were identified to be both mechanism-based inhibitors and substrates of CYP3A and reported to have non-linear pharmacokinetics in clinic[3]. |
| In Vivo | Norverapamil (9 mg/kg; p.o.), a major metabolite of verapamil, has terminal half-life, AUC and Cmax values of 9.4 hours, 260 ng▪h/ml, and 41.6 ng/mL, respectively[4]. Animal Model: Male Sprague-Dawley rats[4] Dosage: 9 mg/kg (Pharmacokinetic Study) Administration: Oral administration Result: t1/2=9.4 hours;AUC=260 ng▪h/mL;Cmax=41.6 ng/mL. |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 586.1ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C26H36N2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 477.03600 |
| Flash Point | 308.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 476.24400 |
| PSA | 72.74000 |
| LogP | 5.94378 |
| Hazard Codes | T+ |
|---|
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |