24257-10-1
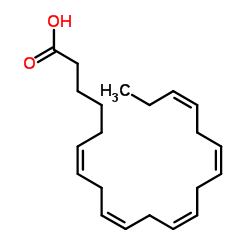
| Name | (6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z,18Z)-henicosa-6,9,12,15,18-pentaenoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
C21:5n-3,6,9,12,15
all-cis-6.9.12.15.18-Heneicosapentaensaeure UNII-HR3EZB17BI Heneicosapentaenoic acid 6,9,12,15,18-Heneicosapentaenoic acid, (6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z,18Z)- 6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z,18Z-heneicosapentaenoic acid (6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z,18Z)-6,9,12,15,18-Henicosapentaenoic acid uncosapentaenoic acid |
| Description | Heneicosapentaenoic Acid (HPA) is a 21:5 omega-3 fatty acid found in trace amounts in the green alga B. pennata and in fish oils. Its chemical composition is similar to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), except that a carbon is extended at the carboxy terminus, placing the first double bond at the δ6 position. HPA can be used to study the importance of double bond position in omega-3 fatty acids. It incorporates phospholipids and triacylglycerols in vivo with the same efficiency as EPA and docosahexaenoic acid, and exhibits a strong inhibitory effect on the synthesis of arachidonic acid from linoleic acid. HPA is a poor substrate for prostaglandin H synthase (PGHS) (cyclooxygenase) and 5-lipoxygenase, but retains the ability to rapidly inactivate PGHS. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 428.0±14.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C21H32O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 316.478 |
| Flash Point | 324.7±15.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 316.240234 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 6.80 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.511 |