189198-30-9
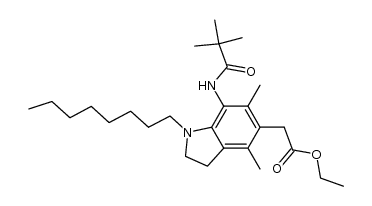
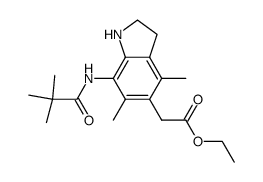
| Name | 2-[7-(2,2-dimethylpropanoylamino)-4,6-dimethyl-1-octyl-2,3-dihydroindol-5-yl]acetic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
UNII-D874R9PZ9T
Pactimibe |
| Description | Pactimibe (CS-505 free base) is a dual ACAT1/2 inhibitor with IC50s of 4.9 μM and 3.0 μM, respectively. Pactimibe (CS-505 free base) inhibits ACAT with IC50s of 2.0 μM, 2.7 μM, 4.7 μM in the liver, macrophages and THP-1 cells, respectively[1]. Pactimibe (CS-505 free base) noncompetitively inhibits oleoyl-CoA with a Ki value of 5.6 μM. Moreover, Pactimibe (CS-505 free base) obviously inhibits cholesteryl ester formation with an IC50 of 6.7 μM. Pactimibe (CS-505 free base) possesses anti-atherosclerotic potential with lowering plasma cholesterol activity[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
ACAT1:4.9 μM (IC50) ACAT2:3.0 μM (IC50) ACAT:2 μM (IC50, in the liver) ACAT:2.7 μM (IC50, in macrophages) ACAT:4.7 μM (IC50, in THP-1 cells) oleoyl-CoA:5.6 μM (Ki) cholesteryl ester formation:6.7 μM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Pactimibe (CS-505 free base) induces moderate ACAT inhibition in monocyte-derived macrophages, leading to the suppression of foam cell formation[2]. |
| In Vivo | Pactimibe (CS-505 free base; 60 and 200 mg/kg/day; oral gavage; twice a day; 12 weeks) induces an inhibition for ACAT-1 and ACAT-2, causing a reduction of plasma cholesterol but no influence on macrophage- or collagen-positive areas[3]. Animal Model: Male C57BL/6J ApoE−/− mice aged 8-week-old[3] Dosage: 60 and 200 mg/kg/day Administration: Oral gavage; twice a day; 12 weeks Result: Decreased plasma cholesterol levels by 39% and 74% at the administration of 60 and 200 mg/kg/day |
| References |
| Density | 1.071 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 604.4ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C25H40N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 416.59700 |
| Flash Point | 319.3ºC |
| Exact Mass | 416.30400 |
| PSA | 69.64000 |
| LogP | 5.77610 |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.86E-15mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.547 |
|
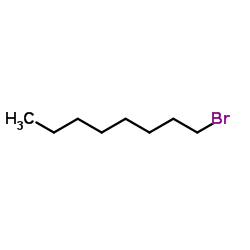
~% 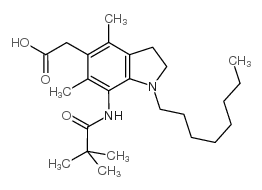
189198-30-9 |
| Literature: Kyoto Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd. Patent: US6063806 A1, 2000 ; |
|
~% 
189198-30-9 |
| Literature: Sankyo Company, Limited Patent: EP1364942 A1, 2003 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 25 ; |
|
~% 
189198-30-9 |
| Literature: Takahashi, Kenji; Kasai, Masayasu; Ohta, Masaru; Shoji, Yoshimichi; Kunishiro, Kazuyoshi; Kanda, Mamoru; Kurahashi, Kazuyoshi; Shirahase, Hiroaki Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2008 , vol. 51, # 15 p. 4823 - 4833 |