2,5-DIMETHYLTETRAHYDROFURAN
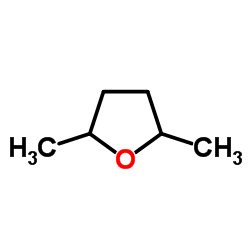
2,5-DIMETHYLTETRAHYDROFURAN structure
|
Common Name | 2,5-DIMETHYLTETRAHYDROFURAN | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1003-38-9 | Molecular Weight | 100.159 | |
| Density | 0.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 91.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12O | Melting Point | -45ºC | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 26.7±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS02 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
| Name | 2,5-dimethyltetrahydrofuran |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 0.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 91.0±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | -45ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12O |
| Molecular Weight | 100.159 |
| Flash Point | 26.7±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 100.088814 |
| PSA | 9.23000 |
| LogP | 1.31 |
| Vapour Pressure | 62.1±0.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.407 |
| InChIKey | OXMIDRBAFOEOQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC1CCC(C)O1 |
| Symbol |

GHS02 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H226 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R10;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S16-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | UN 1993 3/PG 3 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 3.2 |
|
Activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 3 channel suppresses adipogenesis.
Endocrinology 156 , 2074-86, (2015) The present study shows that activation of the transient receptor potential vanilloid 3 channel (TRPV3) suppresses adipocyte differentiation. We also found that a major functional catechin compound in... |
|
|
The reverse of the 'repair' reaction of thiols: H-abstraction at carbon by thiyl radicals.
Int. J. Radiat. Biol. Relat. Stud. Phys. Chem. Med. 51(1) , 91-102, (1987) Thiyl radicals (RS) formed by the reaction of radiolytically generated OH radicals with thiols, e.g. 1,4-dithiothreitol (DTT), react with cis- and trans-2,5-dimethyltetrahydrofuran by abstracting an H... |
|
|
One-step catalytic transformation of carbohydrates and cellulosic biomass to 2,5-dimethyltetrahydrofuran for liquid fuels.
ChemSusChem 3(5) , 597-603, (2010) Existing technologies to produce liquid fuels from biomass are typically energy-intensive, multistep processes. Many of these processes use edible biomass as starting material. Carbohydrates, such as ... |
| 2,5-dimethyl-tetrahydro-furan |
| 1,5-dimethyltetrahydrofuran |
| Furan,tetrahydro-2,5-dimethyl |
| 2,5-Dimethyloxolane |
| 2,5-Dimethyltetrahydrofurane |
| Tetrahydro-2,5-dimethylfuran |
| Furan, tetrahydro-2,5-dimethyl- |
| 2,5-DIMETHYLTETRAHYDROFURAN |
| EINECS 213-707-6 |
| MFCD00005369 |

