N-Methylbenzylamine
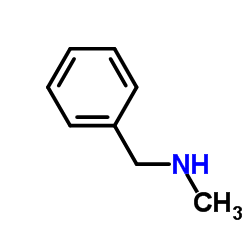
N-Methylbenzylamine structure
|
Common Name | N-Methylbenzylamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 103-67-3 | Molecular Weight | 121.180 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 180.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H11N | Melting Point | -24 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 77.8±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of N-MethylbenzylamineN-methylbenzylamine is a member of phenylmethylamines. N-methylbenzylamine can be found in carrot, which makes N-methylbenzylamine a potential biomarker for the consumption of these food products[1]. |
| Name | N-Methylbenzylamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | N-methylbenzylamine is a member of phenylmethylamines. N-methylbenzylamine can be found in carrot, which makes N-methylbenzylamine a potential biomarker for the consumption of these food products[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 180.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | -24 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C8H11N |
| Molecular Weight | 121.180 |
| Flash Point | 77.8±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 121.089149 |
| PSA | 12.03000 |
| LogP | 1.52 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.9±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.513 |
| InChIKey | RIWRFSMVIUAEBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CNCc1ccccc1 |
| Stability | Stable, but may be air sensitive through reaction with carbon dioxide. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, carbon dioxide. |
| Water Solubility | 65 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H314-H317-H334 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;Goggles;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | C:Corrosive |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R34 |
| Safety Phrases | S23-S26-S36/37/39-S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2735 8/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 8 |
| HS Code | 29214980 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2921499090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2921499090 other aromatic monoamines and their derivatives; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Superparamagnetic core-shells anchored onto graphene oxide grafted with phenylethyl amine as a nano-adsorbent for extraction and enrichment of organophosphorus pesticides from fruit, vegetable and water samples.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1406 , 48-58, (2015) A novel adsorbent composed of silica coated magnetic microparticles (Fe3O4@SiO2) and graphene oxide (GO) functionalized with phenylethyl amine (PEA) was synthesized and characterized using Fourier tra... |
|
|
New procedure of selected biogenic amines determination in wine samples by HPLC.
Anal. Chim. Acta 834 , 58-66, (2014) A new procedure for determination of biogenic amines (BA): histamine, phenethylamine, tyramine and tryptamine, based on the derivatization reaction with 2-chloro-1,3-dinitro-5-(trifluoromethyl)-benzen... |
|
|
Structural analysis of dopamine- and amphetamine-induced depolarization currents in the human dopamine transporter.
ACS Chem. Neurosci. 6(4) , 551-8, (2015) Amphetamine (AMPH) induces depolarizing currents through the human dopamine transporter (hDAT). Recently we discovered that the S(+) enantiomer of AMPH induces a current through hDAT that persists lon... |
| BENZYLAMINE, N-METHYL |
| Benzenemethanamine, N-methyl- |
| N-Mehtylbenzylamine |
| N-Methy-N-benzylamine |
| N-Methylbenzylamine |
| N-benzyl-N-methyl-amine |
| N-Benzylmethylamine |
| EINECS 203-133-4 |
| N-Methylbenzylamin |
| N-methylbenzenemethanamine |
| N-Methyl-1-phenylmethanamine |
| BENZYL METHYLAMINE |
| methylbenzylamine |
| N-methyl-benzylamine |
| NMBA |
| Benzylmethylamine |
| omega-Methylaminotoluene |
| MFCD00008289 |
| N-benzyl-N-methylamine |
| N-Methyl Benylamine |
| ω-Methylaminotoluene |
 CAS#:622-29-7
CAS#:622-29-7 CAS#:3695-02-1
CAS#:3695-02-1 CAS#:6343-54-0
CAS#:6343-54-0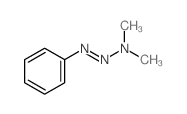 CAS#:7227-91-0
CAS#:7227-91-0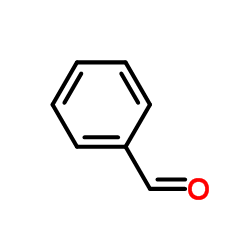 CAS#:100-52-7
CAS#:100-52-7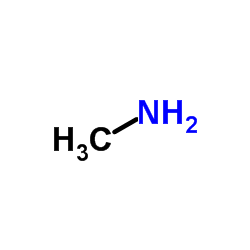 CAS#:74-89-5
CAS#:74-89-5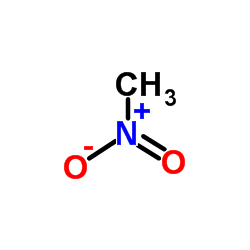 CAS#:75-52-5
CAS#:75-52-5 CAS#:81616-14-0
CAS#:81616-14-0 CAS#:88070-48-8
CAS#:88070-48-8![2-[benzyl(methyl)amino]-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethanone structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/399/108976-12-1.png) CAS#:108976-12-1
CAS#:108976-12-1 CAS#:111831-90-4
CAS#:111831-90-4![[benzyl(methyl)amino]methylphosphonic acid structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/186/107020-03-1.png) CAS#:107020-03-1
CAS#:107020-03-1 CAS#:101-47-3
CAS#:101-47-3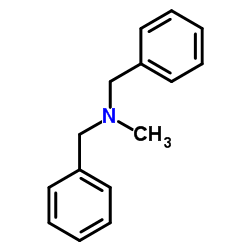 CAS#:102-05-6
CAS#:102-05-6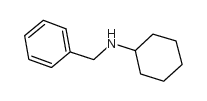 CAS#:4383-25-9
CAS#:4383-25-9 CAS#:2211-66-7
CAS#:2211-66-7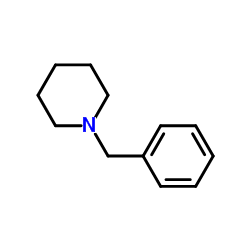 CAS#:2905-56-8
CAS#:2905-56-8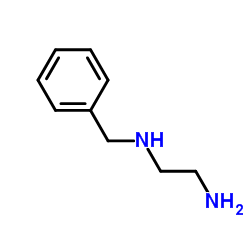 CAS#:4152-09-4
CAS#:4152-09-4
