4-Chlorobenzaldehyde
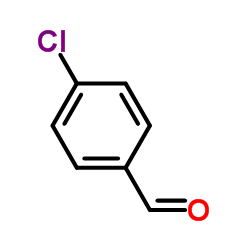
4-Chlorobenzaldehyde structure
|
Common Name | 4-Chlorobenzaldehyde | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 104-88-1 | Molecular Weight | 140.567 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 213.7±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H5ClO | Melting Point | 46 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 87.8±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
| Name | 4-Chlorobenzaldehyde |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 213.7±13.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 46 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C7H5ClO |
| Molecular Weight | 140.567 |
| Flash Point | 87.8±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 140.002899 |
| PSA | 17.07000 |
| LogP | 2.21 |
| Vapour density | 0.6 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.2±0.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.585 |
| Stability | Stable, but air and light-sensitive. Incompatible with strong bases, strong reducing agents, strong oxidizing agents. |
| Water Solubility | 935 mg/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22;R36/38;R51/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S61-S37/39-S36 |
| RIDADR | UN 1219 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 2 |
| RTECS | CU5076000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 9 |
| HS Code | 2913000090 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2913000090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS: 2913000090 halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives of products of heading 2912 Educational tariff:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Regulatory conditions:none Most favored nation tariff:5.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
A universal quantitative ¹H nuclear magnetic resonance (qNMR) method for assessing the purity of dammarane-type ginsenosides.
Phytochem. Anal. 26(1) , 8-14, (2014) Quantitative (1)H-NMR (qNMR) is a well-established method for quantitative analysis and purity tests. Applications have been reported in many areas, such as natural products, foods and beverages, meta... |
|
|
Acetalization allows the photoheterolysis of the Ar-Cl bond in chlorobenzaldehydes and chloroacetophenones.
J. Org. Chem. 77(20) , 9094-101, (2012) The nonaccessibility of phenyl cations by irradiation of electron-poor aryl chlorides was circumvented by transforming the carbonyl group of aromatic ketones or aldehydes into the corresponding 1,3-di... |
|
|
Growth of Thin, Anisotropic, π-Conjugated Molecular Films by Stepwise "Click" Assembly of Molecular Building Blocks: Characterizing Reaction Yield, Surface Coverage, and Film Thickness versus Addition Step Number.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137 , 8819-28, (2015) We report the systematic characterization of anisotropic, π-conjugated oligophenyleneimine (OPI) films synthesized using stepwise imine condensation, or "click" chemistry. Film synthesis began with a ... |
| AMMONIUM STANDARD |
| AMMONIA WATER |
| 4-chloro-benzaldehyde |
| EINECS 203-247-4 |
| 4-Fluorobenzaldehyde |
| AMMONIA GAS |
| 4-Chlorbenzaldehyd |
| AQUEOUS AMMONIA |
| 4-Chlorobenzaldehyde |
| p-Fluorobenzaldehyde |
| Benzaldehyde, 4-chloro- |
| para-chloro-benzaldehyde |
| p-chlorobenzenecarboxaldehyde |
| PCAD |
| AMMONIA NO 2 |
| AMMONIA NO 1 |
| MFCD00011418 |
| p-Chlorobenzaldehyde |
| AMMONIUM LIQUOR |
 CAS#:106-39-8
CAS#:106-39-8 CAS#:201230-82-2
CAS#:201230-82-2 CAS#:637-87-6
CAS#:637-87-6 CAS#:13086-93-6
CAS#:13086-93-6 CAS#:1878-66-6
CAS#:1878-66-6 CAS#:10359-09-8
CAS#:10359-09-8 CAS#:623-03-0
CAS#:623-03-0 CAS#:873-76-7
CAS#:873-76-7 CAS#:14062-80-7
CAS#:14062-80-7 CAS#:106-43-4
CAS#:106-43-4![4-[(4-chlorophenyl)methyl]isoquinoline structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/121/104755-77-3.png) CAS#:104755-77-3
CAS#:104755-77-3![N-[(4-chlorophenyl)methyl]benzenesulfonamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/001/10504-97-9.png) CAS#:10504-97-9
CAS#:10504-97-9 CAS#:837-18-3
CAS#:837-18-3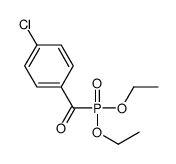 CAS#:10570-46-4
CAS#:10570-46-4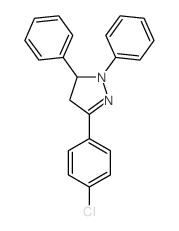 CAS#:10180-02-6
CAS#:10180-02-6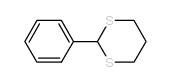 CAS#:5425-44-5
CAS#:5425-44-5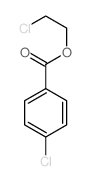 CAS#:1078-32-6
CAS#:1078-32-6 CAS#:106873-17-0
CAS#:106873-17-0 CAS#:110677-45-7
CAS#:110677-45-7
