Ipenoxazone
Modify Date: 2024-01-08 15:23:42
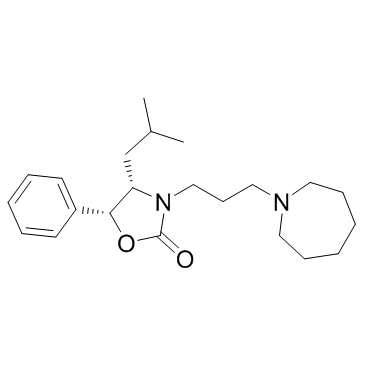
Ipenoxazone structure
|
Common Name | Ipenoxazone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 104454-71-9 | Molecular Weight | 358.51800 | |
| Density | 1.03g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 532.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C22H34N2O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 275.8ºC | |
Use of IpenoxazoneIpenoxazone is a potent and centrally acting muscle relaxant. |
| Name | Ipenoxazone |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ipenoxazone is a potent and centrally acting muscle relaxant. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | Ipenoxazone is a potent and centrally acting muscle relaxant[1]. An intravenous injection of 2 mg/kg Ipenoxazone causes a reduction of electromyographic activity which reaches a maximum within 3 min after the injection. Within 1 min after the injection of Ipenoxazone at a dose of 4 mg/kg, the blood pressure changes from a control level of 138±9 mmHg to a minimum level of 98±9 mmHg (n=6) but it rapidly returns to the control level within 1 to 2 min, while the rigidity is still reduced significantly at that time. High doses (greater than 30 mg/kg i.p.) of Ipenoxazone produces a transient and dose-dependent sedation in almost all mice about 5 min after its administration[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Experiments are performed on 31 adult male rats (Wistar 310 to 430 g, 3 to 7 months of age) anesthetized with chloralose-urethane (50 and 500 mg/kg i.p., respectively). Ipenoxazone is administrated i.v. at 0.05 to 0.1 mL/100 g body weight (20 to 40 s per injection). These four different doses of Ipenoxazone (0.3, 1, 3 and 10 mg/kg) are administrated cumulatively, from small doses to larger doses. It is usually waited about 10 to 30 min between each trial or until all effects of the drug on the bladder have disappeared[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.03g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 532.4ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C22H34N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 358.51800 |
| Flash Point | 275.8ºC |
| Exact Mass | 358.26200 |
| PSA | 32.78000 |
| LogP | 4.73650 |
| Vapour Pressure | 2.05E-11mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.517 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Ipenoglan |
| NC-1200 |
| (4S,5R)-3-[3-(Hexahydro-1H-azepin-1-yl)propyl]-4-(2-methylpropyl)-5-phenyl-2-oxazolidinone |
| MLV 6976 |